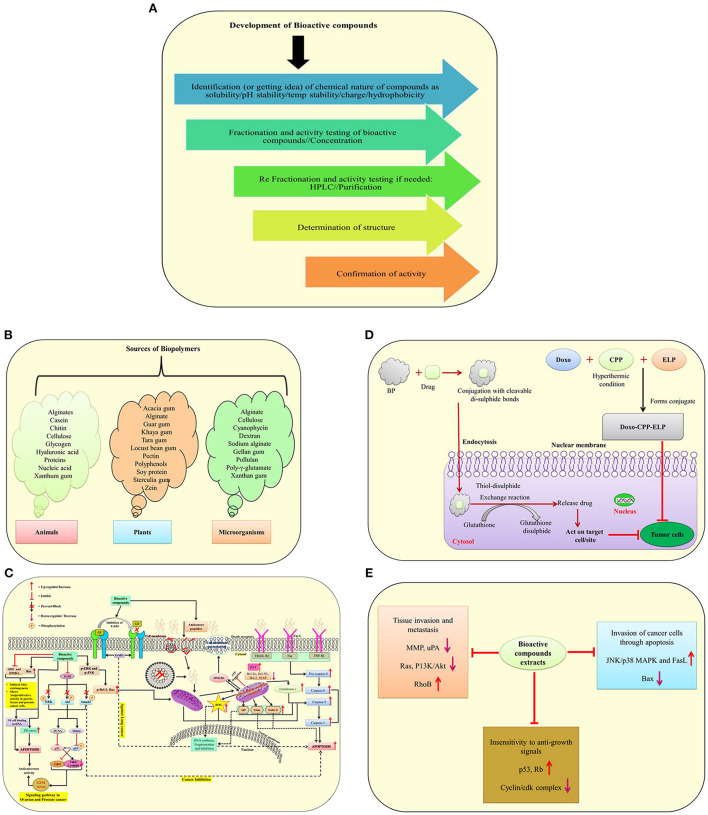
Figure 2.
A schematic illustration of bioactive molecule sources and development, as well as their involvement in drug delivery systems and molecular mechanisms against different cancer cells. (A) Development of bioactive compounds; (B) Sources of biopolymers from plants, animals and microorganisms; (C) Mode of action of anticancerous molecules via TGF–β signaling pathway, death receptor, mitochondrial receptor–induced pathways against cancer cells; (D) A mechanism of suppressing tumor cells using biopolymers in conjunction with drugs; (E) The effect of bioactive molecules from plant extracts on the underlying mechanisms of cancer development [modified and adapted from Lin et al. (76)]. ODC, Ornithine decarboxylase; DMBA, 7,12-Dimethylbenz(α)anthracene; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; NF-Kb, Transcription factor; p-ERK, Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; ENK, c-Jun-N terminal kinase; AIF, Apoptosis-inducing factor; FasL, Fas Ligand; ErbB3, Receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor beta; ERK, Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; AKT1, Serine/threonine-protein kinase; SMAD2, SMAD family member 2; Mdm2, Mouse double minute 2 homolog; PCNA, Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; p53 and p21, Tumor protein; WAF1/CIP1, Wildtype activating factor-1/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory protein-1; cdc2, Cell division cycle 2; HMGB1, High mobility group box 1; Smac, Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; EndoG, Endonuclease G; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; TRAIL, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TNF RI, Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; Rb, Retinoblastoma protein; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; uPA, Urokinase plasminogen activator; BP, Biopolymers.