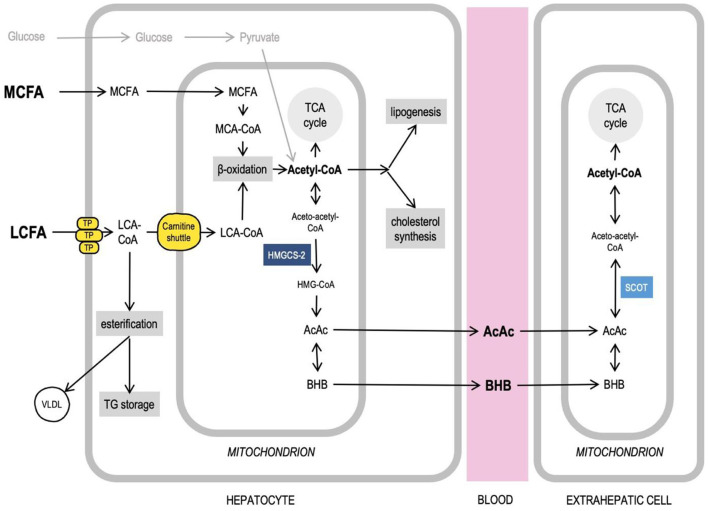
Figure 1.
Medium-chain fatty acids, acetyl-CoA, and intersecting liver metabolic pathways. Long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) and medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are handled by the cells differently. MCFAs do not require transport proteins (TP) to cross membranes, get activated and undergo oxidation in mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA can feed TCA cycle, ketogenesis, lipogenesis, cholesterol synthesis. Excess LCFAs can be esterified to be stored in liver and excreted as VLDL particles. More details in text. AcAc, acetoacetate; Acetyl-CoA, acetyl-Coenzyme A; βHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; HMG-CoA, β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A; HMGCS-2, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2; LCA-CoA, long-chain acyl-Coenzyme A; LCFA, long-chain fatty acids; MCA-CoA, medium-chain acyl-Coenzyme A; MCFA, medium-chain fatty acids; SCOT, Succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid CoA transferase; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle; TG, triglycerides; TP, transport proteins (see details in text); VLDL, very low density lipoprotein.