FIGURE 2.
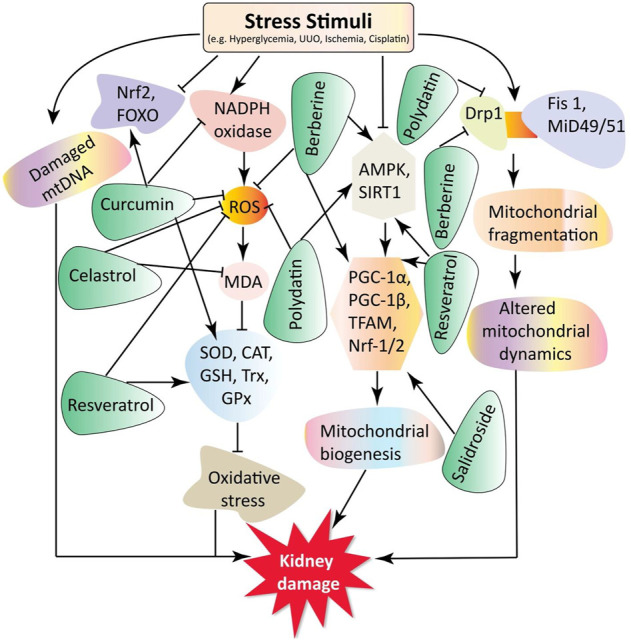
This schematic representation indicates that stress stimuli like HG, UUO, cisplatin, and ischemia regulate various pathological conditions involving oxidative stress, mitochondrial biogenesis, mtDNA damage, and altered mitochondrial dynamics. These ultimately lead to renal damage. The small molecule rotenone reduces mtDNA damage and ROS production. In addition, celastrol reduces the ROS and MDA oxidative stress markers. Polydatin, berberine, and resveratrol decrease ROS production. Salidroside increases SIRT1 and PGC-1α expression, resulting in mitochondrial biogenesis, enhancing and protecting the kidneys. Curcumin and resveratrol increase the transcription of antioxidants markers SOD, CAT, GSS, GPX, and Trx. Moreover, berberine and resveratrol increase the expression of mitochondrial biogenesis markers PGC-1α, TFAM, Nrf-1, and Nrf-2. Furthermore, polydatin decreases the expression of mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 and preserves kidney function. Key: DN, diabetic nephropathy; Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; GSH, glutathione; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GM, gentamycin; HN, hyperuricemic nephropathy; MDA, malondialdehyde; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; Nrf-1 and Nrf-2, nuclear respiratory factors 1 and 2; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SIRT1, silent mating type information regulation 2 homologs 1; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Trx, thioredoxin; TFAM, transcription factor A of mitochondria.
