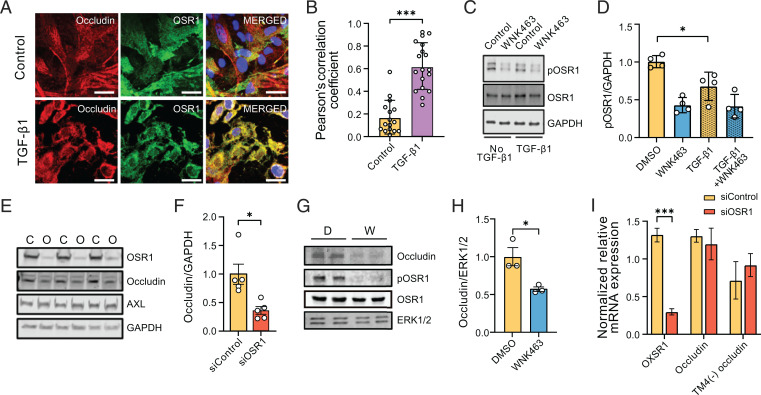
Fig. 4.
WNK1/OSR1 collaborate with TGF-β to regulate tight junction turnover and localization and function of occludin. (A) Representative confocal images of immuno-fluorescently labeled endogenous occludin (red), OSR1 (green), and nucleus (DAPI: blue) in primary HUVECs with or without TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) stimulation (no TGF-β1, n = 16; TGF-β1, n = 18). Merged panel (yellow) shows colocalization between occludin and OSR1. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Corresponding quantification of images in A colocalizing pixels was done by measuring Pearson’s correlation coefficient shows increased colocalization with TGF-β1 treatment. (C) Representative Western blots show expression of phosphorylated Ser325 OSR1 in HUVECs treated with WNK463 (1 µM) and/or TGF-β1 (1 ng/mL). (D) Corresponding quantification of images in C shows decreased phosphorylated OSR1 (pOSR1) upon TGF-β1 treatment; n = 4. (E) Representative Western blots of occludin protein levels upon OSR1 knockdown in HDMECs. C, control siRNA; O, OSR1 siRNA. (F) Corresponding quantification of images in E shows decreased occludin expression 72 h after siOSR1 treatment compared with siControl (control siRNA), n = 5. (G) Representative Western blots show occludin protein levels treated with WNK463 compared with DMSO control. D, DMSO; W, WNK463. (H) Corresponding quantification of Western blots in G shows decreased occludin amount in WNK463-treated condition compared with DMSO control in HUVECs; n = 3. (I) Quantification of 18S-normalized relative mRNA expression in HDMECs shows no change in mRNA expression of occludin or TM-4(−) occludin (occludin isoform lacking fourth transmembrane domain) treated with siOSR1 compared with siControl; n = 5. Data are represented as mean ± SE analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0005.