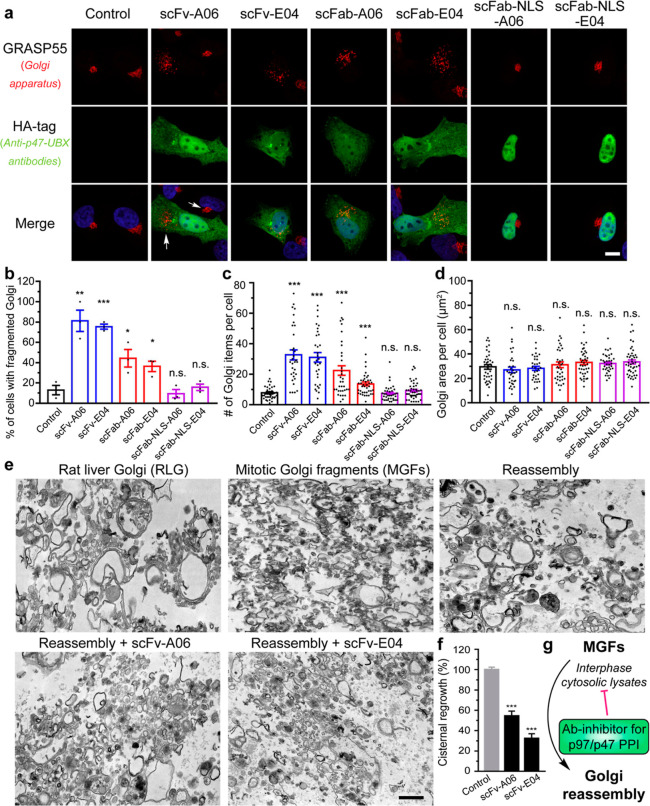
Figure 4.
Anti-p47-UBX antibody fragments disrupt the Golgi structure by inhibiting its post-mitotic reassembly process. (a) Representative immunofluorescence images of HeLa cells transfected with HA-tagged anti-p47-UBX antibody fragments for 24 h and stained with an antibody to Golgi marker GRASP55. Scale bar, 10 μm. (b–d) Quantification of GRASP55 for the percentage of cells with fragmented Golgi (b), number of Golgi items per cell (c), and the Golgi area per cell (d). Data are shown as mean ± SEM from N = 3 independent experiments. (e) Representative transmission electron microscopy images of RLG, MGF (RLG treated with mitotic cytosol), and reassembled samples (MGF treated with interphase cytosol). In brief, RLG membranes were fragmented by treatment with mitotic HeLa cytosol, and MGFs were reisolated and incubated with interphase cytosol alone or in the presence of recombinant anti-p47-UBX scFvs. Scale bar, 500 nm. (f) Quantification of the cisternal regrowth in (e). Results are shown as the mean percentage of membranes in cisternae ±SEM, where 0% represents cisternal regrowth in MGF (10.8 ± 1.7% of membranes in cisternae) and 100% represents cisternal regrowth of MGFs incubated with interphase cytosol alone (56.7 ± 1.1% of membranes in cisternae). Statistical analyses were performed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; and n.s., no significance. (g) Scheme showing antibody fragment inhibitors of p97/p47 PPI-inhibiting Golgi reassembly.