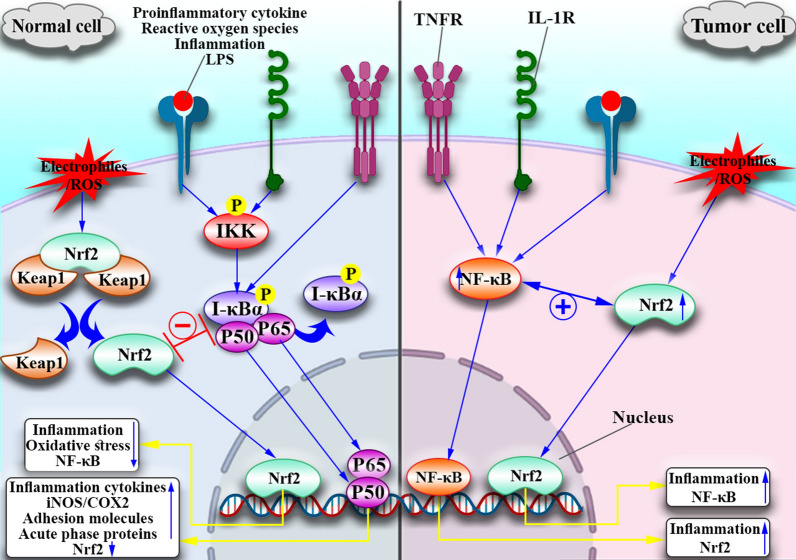
Fig. 4.
Cross-Talk Between Nrf2 And NF-κΒ. In response to NF-κΒ activators such as pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α), LPS, inflammation, and ROS, normal cells induce phosphorylation of IKKβ, which causes phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα (a negative regulator of NF-κΒ). Then NF-κΒ (P65/P50) migrates to the nucleus and triggers gene transcription involved in inflammation. However, Nrf2 suppresses NF-κΒ activation and inflammation directly through Keap1 attachment, or Ho-1 induces P65 suppression. Conversely, in malignant cells, Nrf2 and NF-κΒ act synergistically