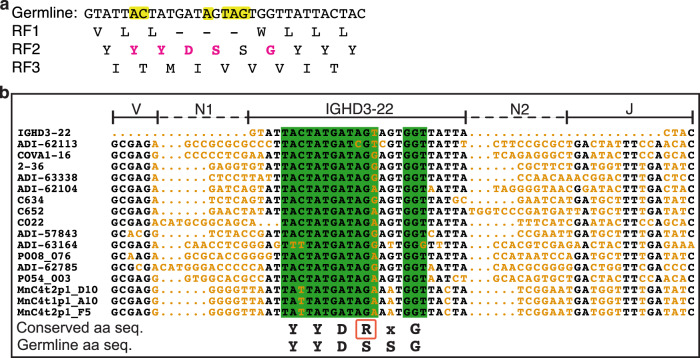
Fig. 4. Reading frames (RFs) and sequence alignment of IGHD3-22.
a Three possible RFs of the IGHD3-22 germline sequence were translated into amino-acid sequences. Only RF2 encodes the YYDRxG motif (magenta). Nucleotides highlighted in yellow in the germline DNA sequence indicate sites where somatic hypermutations are often found in YYDRxG neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. – indicates a stop codon. b Alignment of YYDRxG coding sequences in CDR H3. Conserved nucleotide sequences are in black, and variable sequences in orange. N additions (N1 and N2) as defined by IMGT junction analysis75 are indicated by dashed lines. IGHD3-22, IGHV(V), and IGHJ (J) regions are indicated by solid lines above the sequences. Sequences in a green background encode the YYDRxG key residues. Conserved YYDRxG sequence and corresponding germline amino-acid sequence (aa seq.) are shown below the sequence alignment panel for comparison. The arginine residue in the YYDRxG motif in a red box resulted from a high co-incidence of somatic mutations. Only the first 16 coding sequences are shown in the sequence alignment to represent 100 such antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.