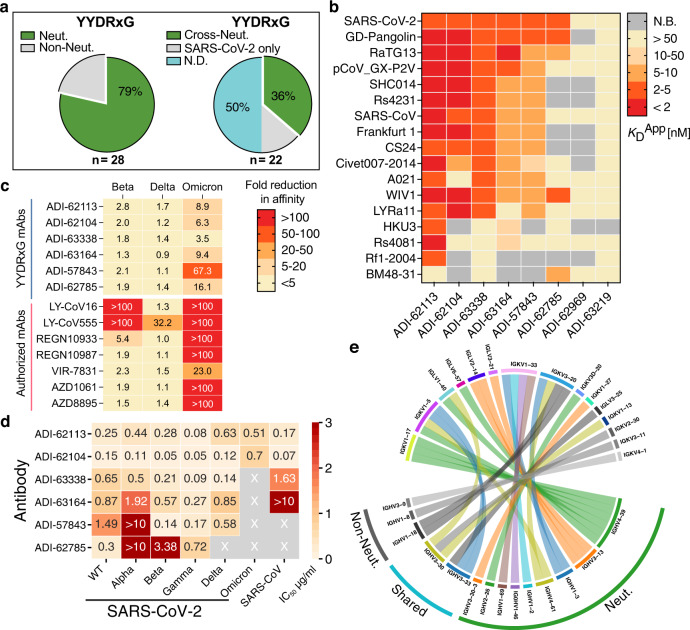
Fig. 5. YYDRxG antibodies are associated with broad neutralization against VOCs including Omicron.
a Neutralization overview of YYDRxG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Antibodies with neutralization data available from this study or from previous publications are included in this analysis. Within 28 YYDRxG antibodies, 22 (79%) exhibit neutralization (Neut.) against SARS-CoV-2 (left). Among these 22 antibodies, 8 (36%) cross-neutralize (Cross-Neut.) SARS-CoV, while 3 (14%) do not (SARS-CoV-2 only); another 11 (50%) have not been tested against SARS-CoV (N.D.) (right). b Cross-reactivity of ADI antibodies with a YYDRxG motif across sarbecoviruses. ADI antibodies were titrated with sarbecovirus RBDs expressed on the yeast surface. Color bars indicate apparent binding affinity (KDApp) as in the key. Red indicates strong binding, yellow indicates weak binding, and gray indicates no detectable binding (N.B.). Most antibodies are cross-reactive with many other sarbecovirus RBDs, except for ADI-63219 and ADI-62969. ADI-62113 showed the broadest spectrum of cross-reactivity to other sarbecoviruses. Titration curves used to determine binding affinities are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5. c YYDRxG antibodies generally preserve their binding to more challenging variants with strong escape mutations or increased transmissibility, such as Beta, Delta, and Omicron, while almost all antibodies under emergency use authorization do not. Kinetics for each antibody in binding to RBDs of the indicated SARS-CoV-2 variants were measured and compared to binding to the RBD of the wildtype ancestral virus. Fold reduction in affinity (KD) was plotted with red indicating substantial loss of binding (>100-fold reduction) and yellow indicating no significant change (<5-fold reduction). Titration curves used to determine binding affinities are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6. d ADI antibodies neutralize SARS-CoV-2, VOCs and SARS-CoV. Neutralization was tested using a pseudovirus assay system. Neutralization potency, i.e., IC50, for each antibody against corresponding viruses are shown on a heatmap with wheat indicating potent neutralization. X indicates weak to no neutralization activity. ADI-63219 and ADI-62969 showed no neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 and are not included in this heatmap. Titration curves used to determine neutralization potency are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. e Distinct combinations of heavy and light variable genes used by neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies. Circos plot showing combinations of heavy and light chain variable genes in each encoded antibody. Colored ribbons represent variable genes encoding neutralizing antibodies (Neut.) while gray indicate non-neutralizing antibodies (Non-Neut.). IGHV3-30, IGHV3-33, and IGKV3-20 were found in both neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies. YYDRxG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 with neutralization data available are included in this analysis (n = 28). Antibody names and CDR H3 sequences of these antibodies are included in Supplementary Table 1.