Figure 5. Hydrophobic interactions mediate binding.
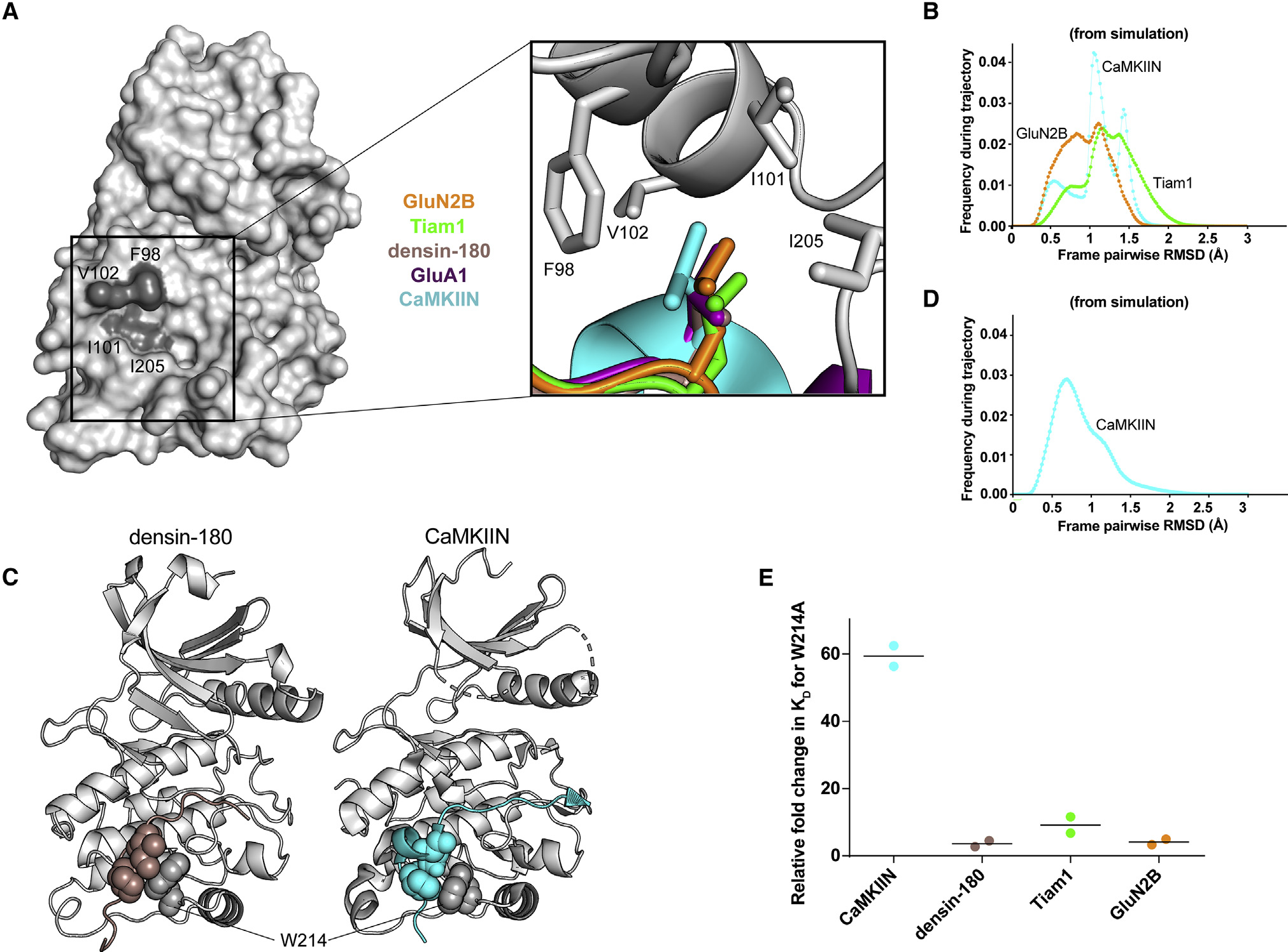
(A) Surface representation of the CaMKII kinase domain, with residues forming the hydrophobic pocket labeled (dark gray). Inset: overlay of leucine residues from all co-crystal structures bound in the hydrophobic pocket.
(B) Histograms of RMSD from MD simulations between every pair of trajectory frames for F98, I101, V102, and I205 with −5 peptide leucine.
(C) Crystal structures with sphere representation of the isoleucine and proline or leucine residues of densin-180 (brown) and CaMKIIN (cyan) docking onto W214 (gray) of the kinase domain.
(D) RMSD histogram from MD simulations for W214 interacting with isoleucine and proline of CaMKIIN.
(E) Kd values were extracted from ITC data, and relative fold changes were calculated by dividing the observed Kd from the mutant (W214A) by the D135N kinase domain. Individual data points are shown, and the line indicates the average.
