Figure 6. Electrostatic interaction with E236 facilitates binding.
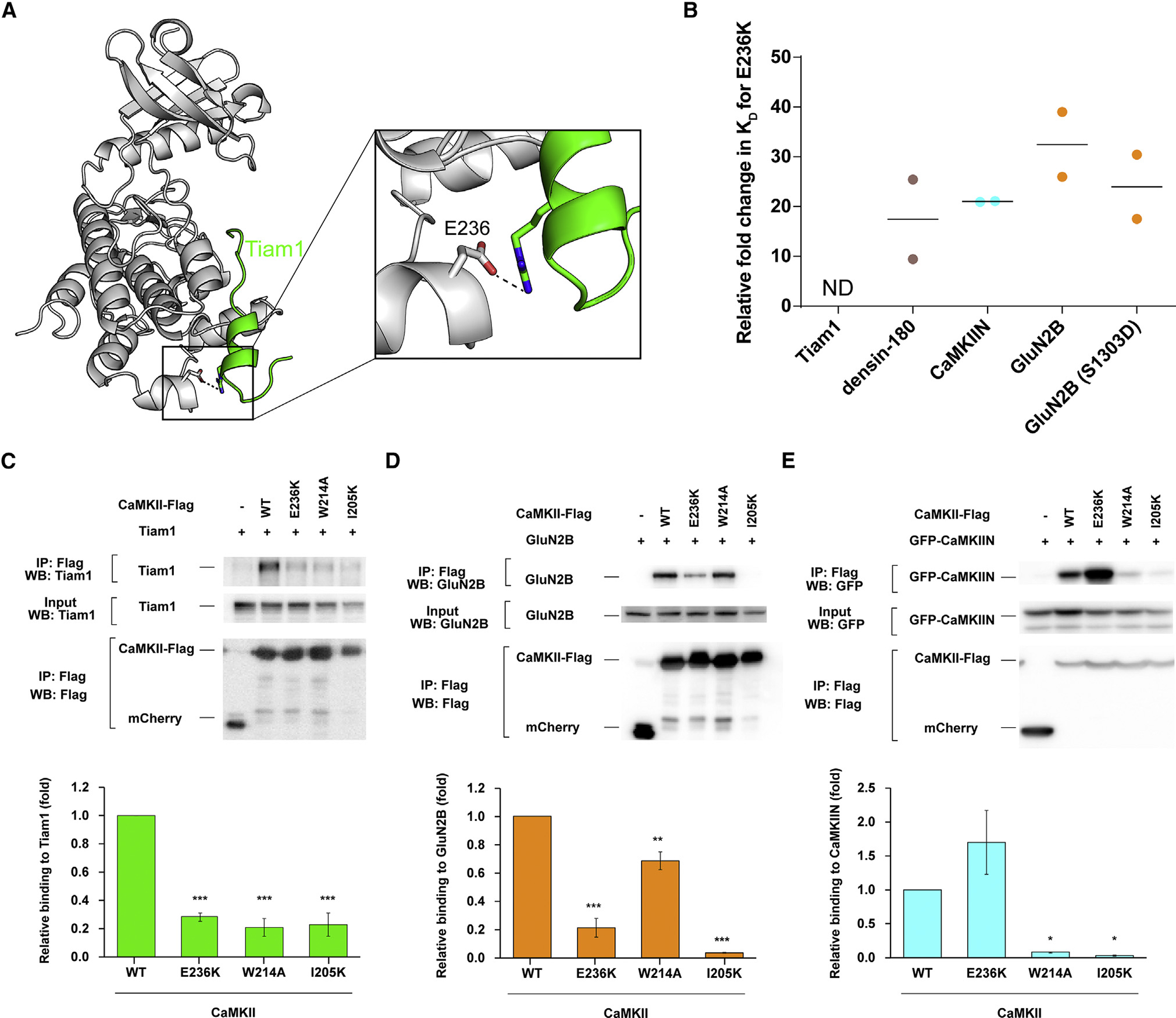
(A) View of the interaction between CaMKII E236 (gray) and Tiam1 R1549 (green).
(B) Kd values were extracted from ITC data, and relative fold changes were calculated by dividing the observed Kd from the mutant (E236K) by the D135N kinase domain. Individual data points are shown, and the line indicates the average.
(C–E) Effects of CaMKII mutations (E236K, W214A, and I205K) on interactions with Tiam1, GluN2B, and CaMKIIN. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-tagged CaMKII variants and Tiam1-mGFP (modified GFP), GluN2B, or EGFP-CaMKIIN. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with FLAG antibody, and samples were immunoblotted with Tiam1, GluN2B, GFP, and FLAG antibodies. Representative blots are shown in the top panels. Quantification of the co-immunoprecipitation from 3 or 4 independent experiments is shown in a graph of (C) Tiam1 (n = 3), (D) GluN2B (n = 3), and (E) CaMKIIN (n = 4). Error bars indicate standard error of the means. The amount of co-immunoprecipitated Tiam1, GluN2B, or CaMKIIN was normalized by the amount in cell lysate and immunoprecipitated CaMKII. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with WT CaMKII; one-way ANOVA with Shaffer’s post hoc test comparisons. WT, wild type; IP, immunoprecipitation.
