Figure 7.
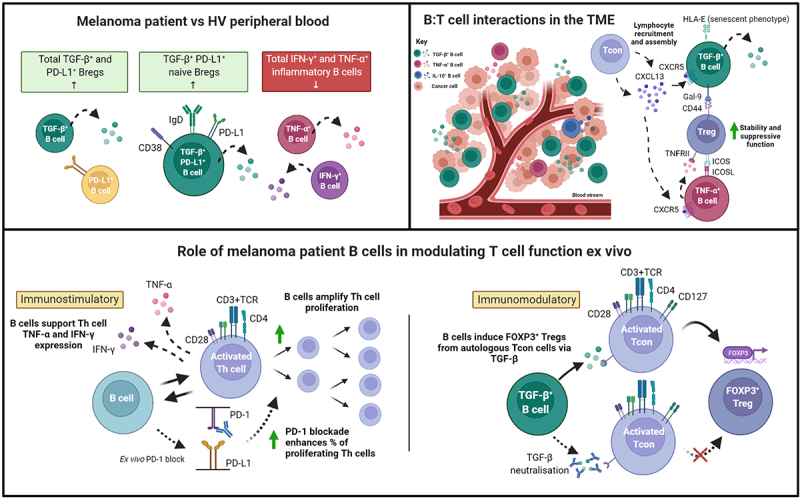
Cytokine-expressing B cells in melanoma are dysregulated in the circulation, engage in crosstalk with Tregs in the TME, and engender immunostimulatory and immunomodulatory influences ex vivo.
Our results identified dysregulation among cytokine-expressing B cells in melanoma patient circulating B cell compartment which favored regulatory phenotypes. We found enriched circulating populations of total TGF-β, total PD-L1 regulatory B cells, and a TGF-β and PD-L1 co-expressingCD19+CD38intIgD+CD27− naïve Breg subset, simultaneous to reduced pro-inflammatoryIFN-γ+ and TNF-α+ B cells in melanoma patients compared to matched healthy volunteers. Within melanoma lesions, TNF-α-expressing B cells were detectable but proportionally reduced compared to those present in the patient circulation, and substantial populations of intratumoral TGF-β+ B cells were detected. TGF-β+ B cells featured a HLA-E+ senescent phenotype and may support the differentiation and maintenance of Tregs in melanoma tumors through expression of Galectin-9. On the other hand, the TNF-α+ TIL-B engaged in crosstalk with Tregs, including via the ICOS/ICOSL axis and TNF-α signaling, which are likely to support the suppressive activity of Tregs in the melanoma TME. Expression of CXCL13 by Tcon cells may participate in the recruitment of both TGF-β+ and TNF-α+ B cells. Finally, ex vivo B:T cell co-cultures demonstrated that patient-derived B cells promoted the proliferation of autologous T-helper cells, which could be further enhanced with anti-PD-1 treatment, and also permitted autologous T-helper cells to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ and TNF-α). In contrast, melanoma patient B cells significantly promoted ex vivo FOXP3+ Treg differentiation from autologous purified CD25−/intCD127+ conventional T-helper cells via TGF-β. Overall, we have established that cytokine-expressing B cells are dysregulated in the circulation of melanoma patients, can infiltrate tumors and engage in crosstalk with and promote Tregs in the TME, while still being able to participate in immunostimulatory T cell functions ex vivo.
