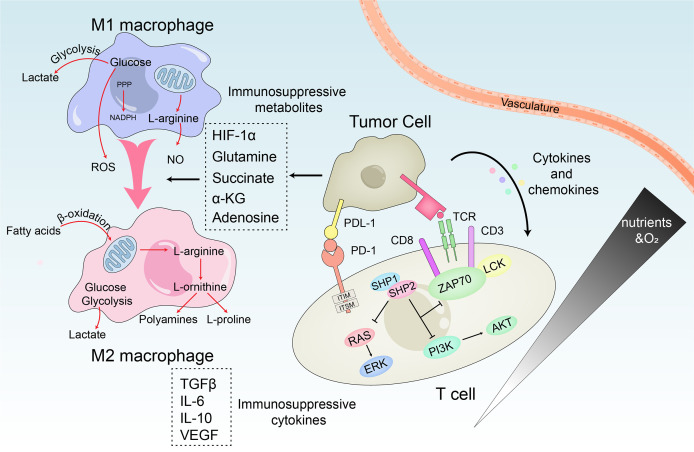
Figure 4.
Metabolic crosstalk within the immunosuppressive microenvironment. M1 macrophages rely on the production of lactate, ROS and NO to kill tumor cells, while M2 macrophages mainly promote tumor growth through β-oxidation of fatty acids and polyamines and L-proline produced by the TCA cycle. In HCC, TME reprogram macrophage metabolism through immunosuppressive metabolites and induces the repolarization of M1 to M2. Similarly, the interaction of immune regulatory cells and cytokines disables the anti-tumor T cell response. PD-1 accompanied with PD-L1 directly inhibits T cell receptor signaling by preventing phosphorylation of ZAP70. Meanwhile, the PI3K/Akt and Ras/MEK/Erk pathways required to initiate T cell activation are also be disrupted.