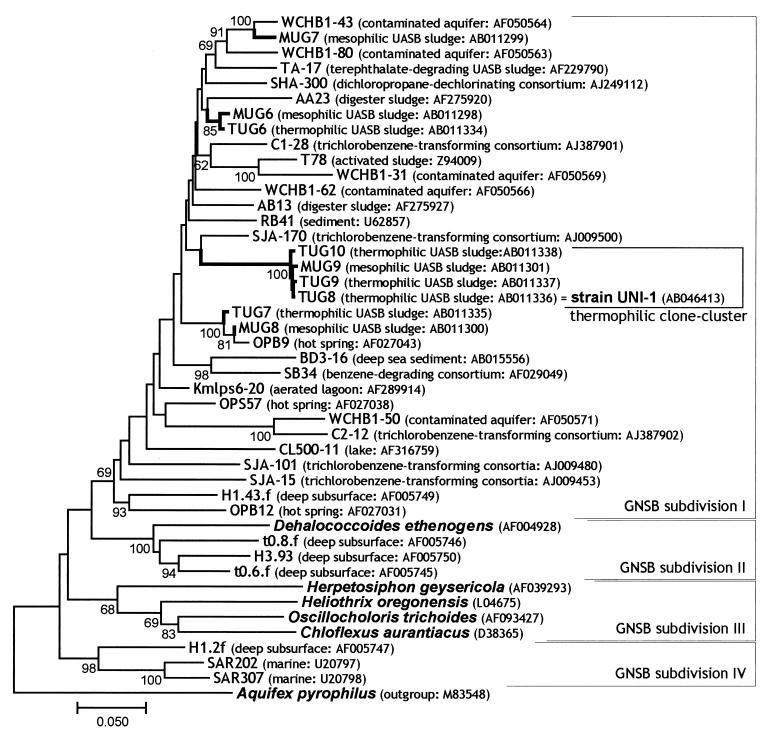
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic tree of GNSB, including environmental clones. The 16S rDNA sequences obtained in the previous study (MUG and TUG clones) and reference sequences were aligned, and phylogenetic trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining method (pairwise analysis). Bar represents 5 nucleotide substitutions per 100 nucleotides in 16S rDNA sequences. The sequence of Aquifex pyrophilus was used to root the tree. Bootstrap values above 50% are indicated at the branch points. The accession number of each reference sequence and the origin of environmental clones are also shown in parentheses. Names of cultivated organisms are shown in bold and italic. Our UASB clones, referred to as thermophilic UASB cluster and strain UNI-1, are shown in a bracket.