FIG. 3.
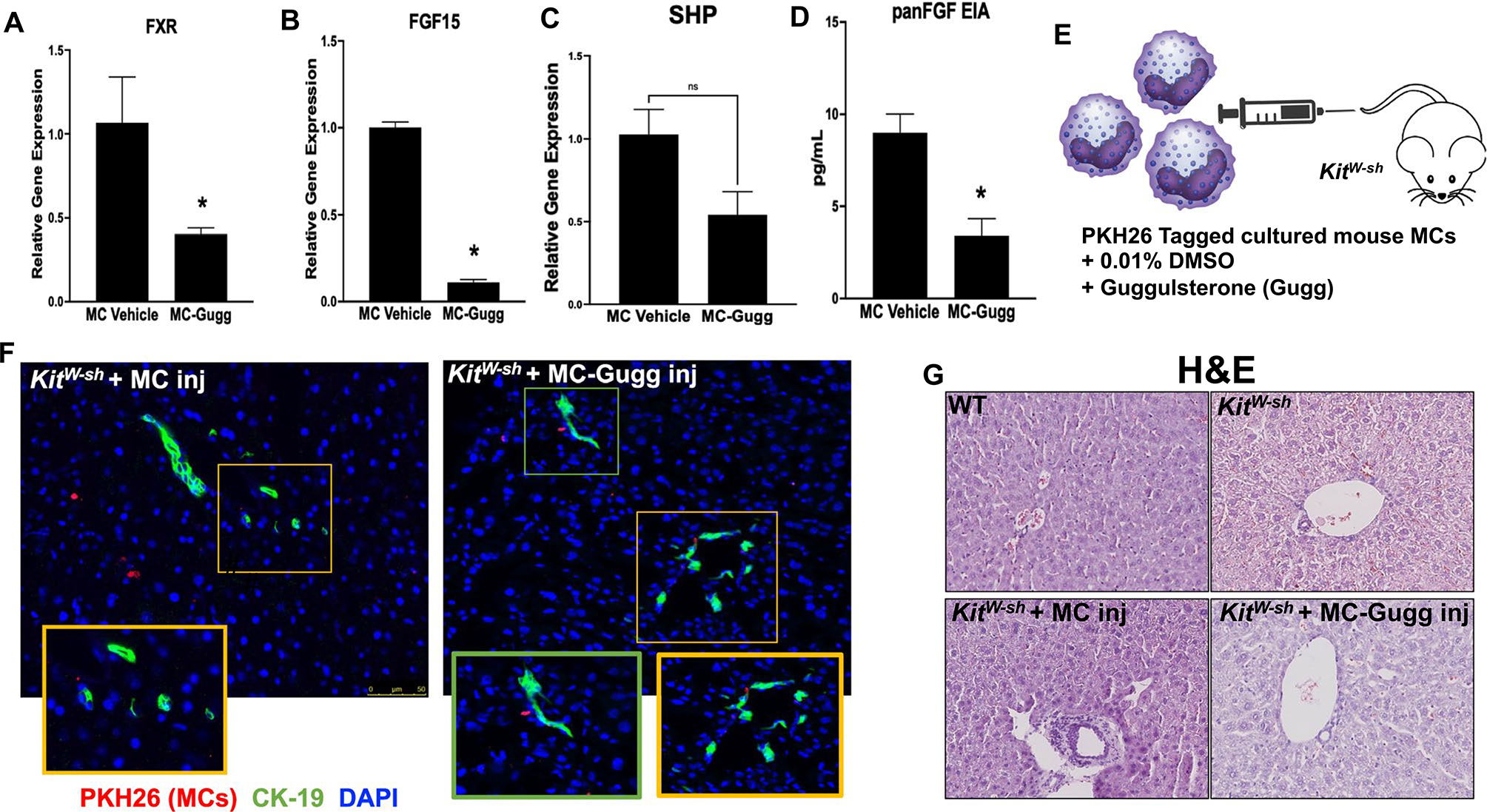
Validation of model and hepatic damage in KitW-sh mice. Cultured MCs (MC/9, ATCC CRL-8306) were stimulated with 0.1% DMSO (vehicle) or 10 μM Z-guggulsterone for 48 hours and (A) FXR, (B) FGF15, (C) SHP mRNA expression, and (D) panFGF secretion were measured. Following treatment, MC-Gugg have reduced (A-C) FXR, FGF15, and SHP mRNA levels, measured by qPCR, and (D) panFGF secretion, measured by EIA, compared with vehicle-treated MCs. (E) Cultured MCs were treated with 0.1% DMSO or guggulsterone (Gugg) and tagged with PKH26 before injection into KitW-sh mice through tail vein. MC migration to the liver was confirmed in KitW-sh mice injected with both (F) vehicle-treated MCs and Z-guggulsterone–treated MCs (MC-Gugg) by immunofluorescence imaging of PKH26 (red) and CK-19 to mark bile ducts (green). (G) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining demonstrates increased hepatic damage and ductular inflammation in KitW-sh + MC that is absent in WT and KitW-sh mice. Hepatic damage is reduced in KitW-sh + MC-Gugg mice. Data are mean ± SEM of n = 4 experiments from n = 2 biological replicates for qPCR and panFGF EIA. *P < 0.05 vs. MC-vehicle. Representative images are presented as ×20 for immunofluorescence, with ×40 zoom boxes, and ×10 for H&E. Abbreviation: Inj, injury.
