FIG. 6.
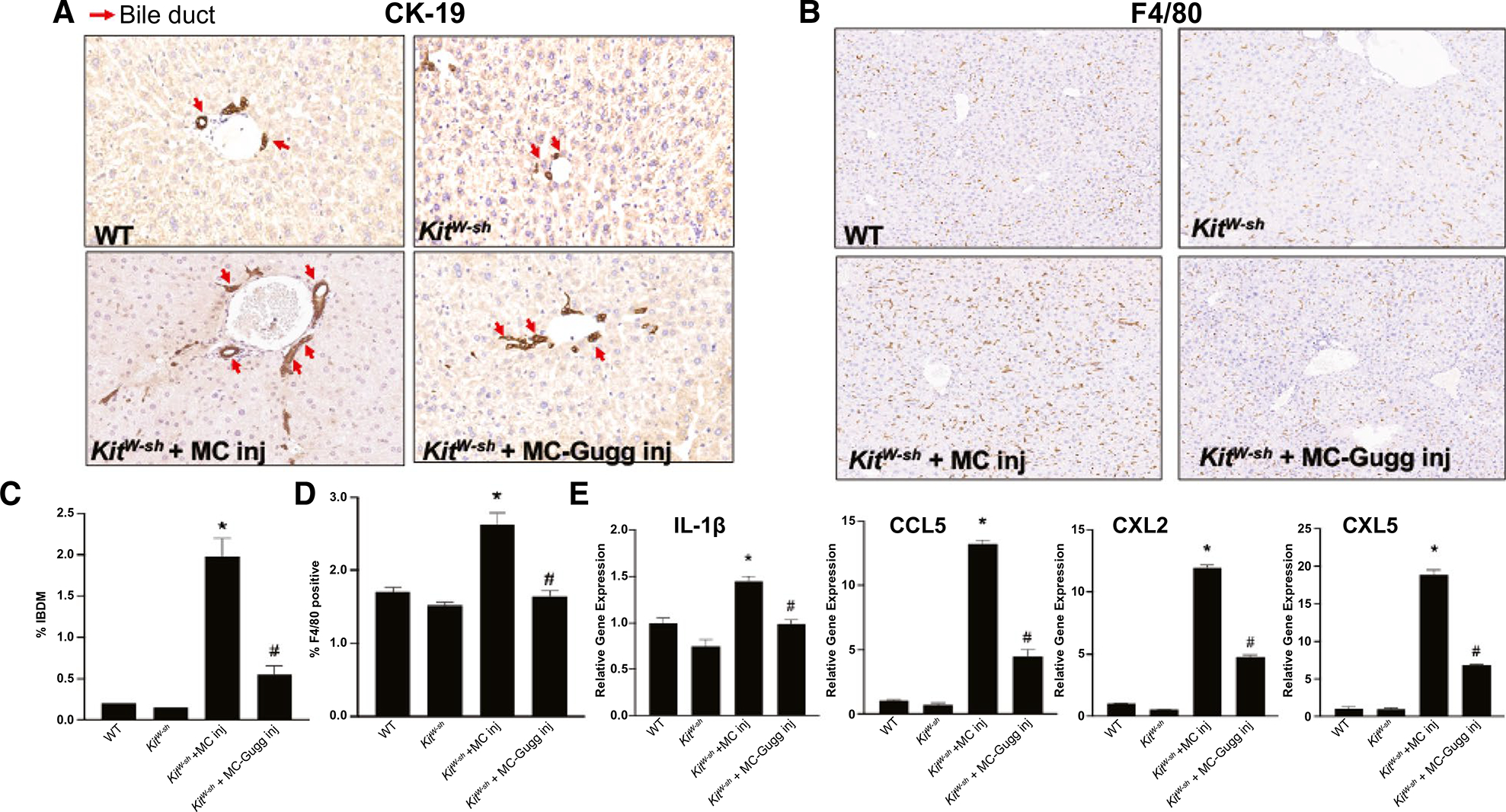
Inhibition of MC-FXR reduces IBDM and inflammation. The effect of MC-FXR inhibition on IBDM and liver inflammation was measured by immunohistochemistry for (A) CK-19 and (B) EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1 mouse homolog (F4/80), respectively, with (C,D) semiquantification. WT and KitW-sh mice display minimal IBDM and F4/80 positive Kupffer cells that increased following MC injection in KitW-sh + MC mice. Inhibition of MC-FXR reduced both IBDM and inflammation. (A) Red arrows indicate CK-19 positive bile ducts. (E) WT and KitW-sh mice have minimal expression of hepatic inflammatory markers IL-1β, CCL5, CXCL2, and CXCL5, whereas KitW-sh + MC mice have increased hepatic inflammatory marker expression that is reduced in KitW-sh + MC-FXR mice. Data are mean ± SEM of n = 10–15 representative images for immunoreactivity semiquantification and of n = 4 experiments for qPCR from 6–8 mice per group. *P < 0.05 vs. WT, #P < 0.05 vs. KitW-sh + MC. All representative images are presented as ×10. Abbreviation: Inj, injury.
