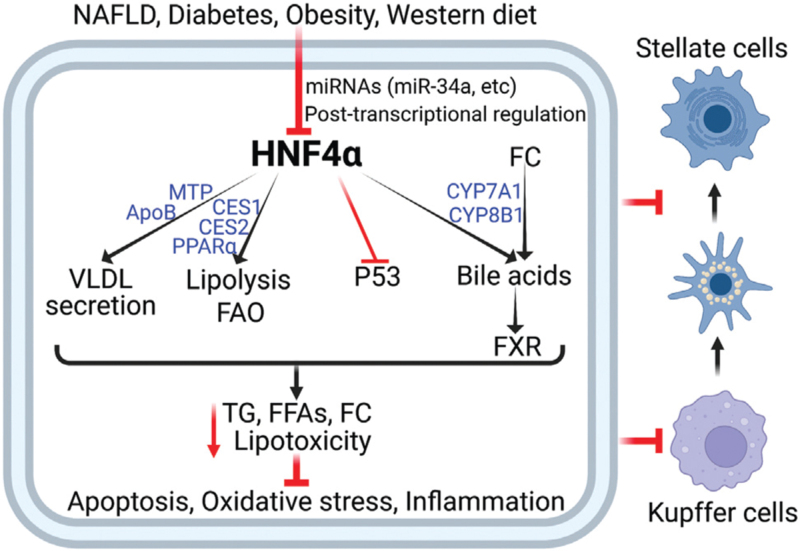
Figure 3.
Hepatic HNF4α regulates the development and progression of NAFLD via multiple pathways. Hepatic HNF4α expression is reduced in NAFLD, diabetes and obesity, and by western diet feeding. HNF4α reduces hepatic lipotoxicity by regulating several pathways, including the induction of lipolysis, FAO, VLDL secretion, and bile acid synthesis. HNF4α also inhibits P53 activity. As a result, hepatic apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrogenesis are inhibited. FC: Free cholesterol; FAO: Fatty acid oxidation; FFAs: Free fatty acids; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; HNF4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; TG: Triglycerides; VLDL: Very low- density lipoprotein.