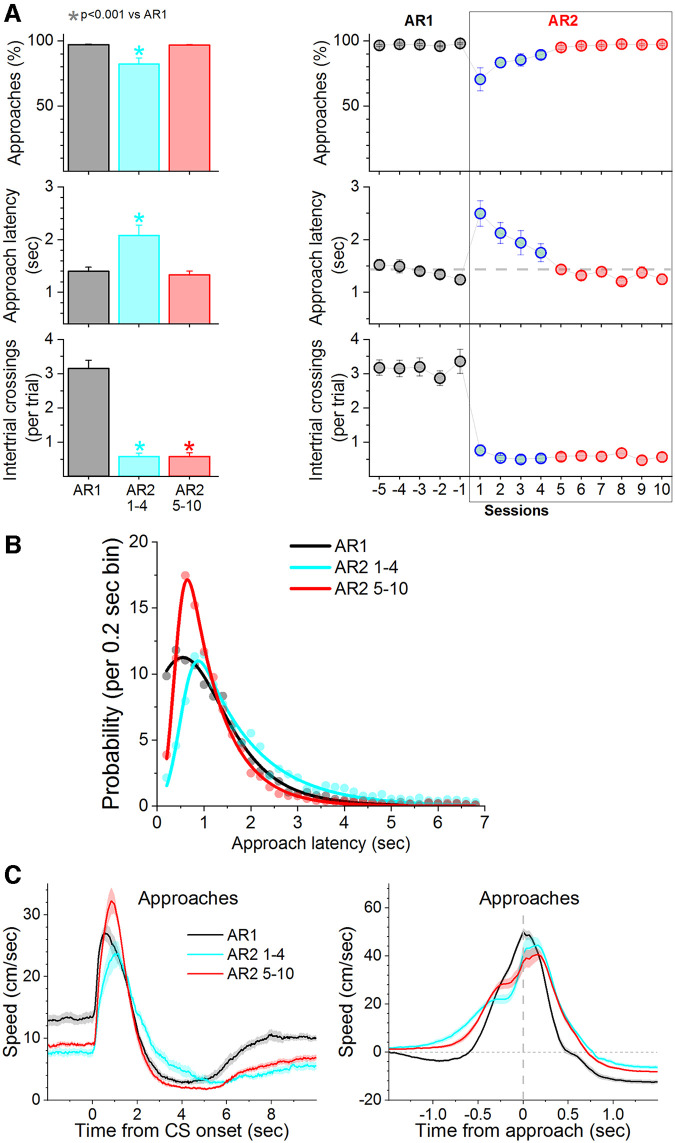
Figure 8.
When the signaled action is an active approach, punishing the unsignaled action leads only to transient caution about producing the signaled action. A, Performance of signaled active approach (AR1) to obtain water (reward) in water-restricted mice. The task is similar to AA1 but mice shuttle during the CS presentation (approach interval) to obtain water instead of avoiding the US. Subsequent training in AR2, which punishes ITCs, led only to brief caution about producing the signaled action (initial 1–4 AA2 sessions; blue) but thereafter (5–10 AA2 sessions; red) caution was not evident in response timing. B, Probability histogram (%) of approach latencies during AA1 and AA2 fitted with an exponential Gaussian. Note the slight rightward shift of the latencies during the initial one to four sessions but subsequently (5–10 sessions) latencies shift left producing a sharp short-latency peak. During AR2, when the action is an approach, mice only display caution transiently. C, Speed traces (mean ± SEM) of active approach responses aligned by the CS onset (left) and baseline-corrected approach responses aligned by the response occurrence (right) during AR1 and AR2 procedures.