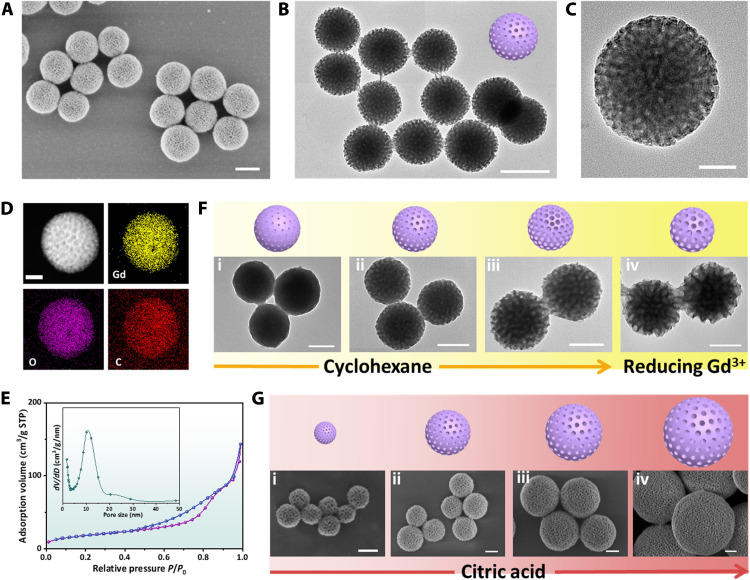
Fig. 1. Microstructure characterization of the DM-Gd(OH)x nanoparticles and controllability of the viscosity-mediated assembly strategy.
(A) SEM, (B and C) TEM images with different magnifications, (D) element mappings, (E) nitrogen sorption isotherms, and pore size distribution of DM-Gd(OH)x (STP means standard temperature and pressure). (F) Scheme illustrations and TEM images of DM-Gd(OH)x nanoparticles with different pore sizes (3 to 20 nm) by tuning the amount of cyclohexane: (i) 0 ml, (ii) 2.0 ml, (iii) 4.0 ml, and (iv) 4.0 ml (the amount of GdCl3·6H2O were also decreased from 15 to 5 mg). (G) Scheme illustrations and SEM images of DM-Gd(OH)x nanoparticles with different particle sizes (80 to 500 nm) by simply tuning the concentration of citric acid: (i) 0.1 mg/ml, (ii) 0.2 mg/ml, (iii) 0.3 mg/ml, and (iv) 0.4 mg/ml. Scale bars, 50 nm (C and D), 100 nm (F and G), and 200 nm (A and B).