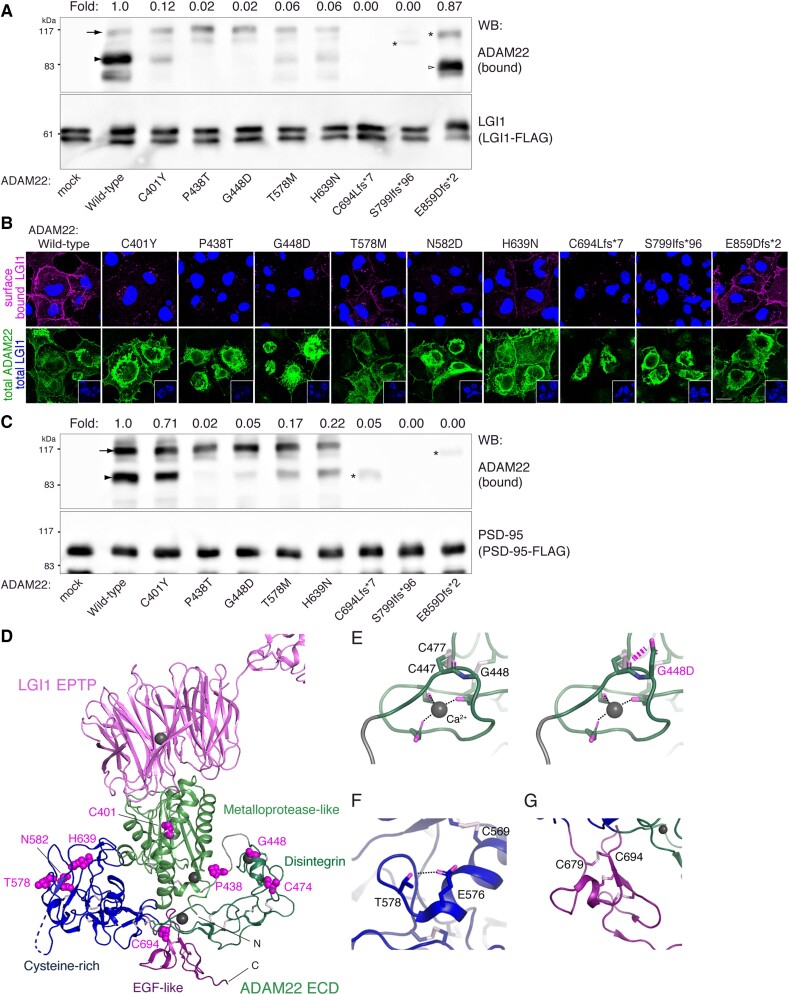
Figure 3.
LGI1- and PSD-95-binding activities of ADAM22 variants. (A) The interaction of ADAM22 variants with LGI1-FLAG was examined by immunoprecipitation with FLAG antibody in lysates derived from COS7 cells transiently co-transfected with wild-type or indicated variant ADAM22 and LGI1-FLAG. ADAM22 variants besides E859Dfs*2 showed reduced or no binding to LGI1. Immature ADAM22 (arrow and asterisks) was often observed when overexpressed in cells and seemed to be non-specifically precipitated under the conditions. In the rodent brain lysate, immature forms are hardly detected.4 (B) LGI1-FLAG and ADAM22 variants were co-expressed and cell-surface bound LGI1 through ADAM22 was live-labelled by anti-FLAG antibody. After fixation and permeabilization of cells, protein expression of ADAM22 (total) and LGI1 (in insets; total) was validated. (C) The interaction of ADAM22 variants with PSD-95 was investigated as in A. E859DfsTer2 selectively lost the binding to PSD-95. Extracellular missense variants showed various levels of PSD-95 binding, according to their expression levels. Fold changes in LGI1 (A) or PSD-95 (C) binding of variants relative to the wild-type are shown. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Mapping of eight ADAM22 variants on the LGI1 EPTP-ADAM22 structure. The corresponding amino-acid residues are shown. (E–G) Close-up views of G448 (E), T578 (F) and C694 (G). The G448D mutation causes a steric hindrance to C447 (E, right) and impairs the disulphide bond formation between C447 and C477, which supports the Ca2+ coordination (E, left). The T578M mutation impairs the hydrogen bond formation between T578 and E576 (F). The C694L mutation disrupts the disulphide bond formation between C679 and C694 (G). Note that provided immunoblots have been cropped; full images are provided in Supplementary Fig. 6. ECD = extracellular domain of ADAM22.