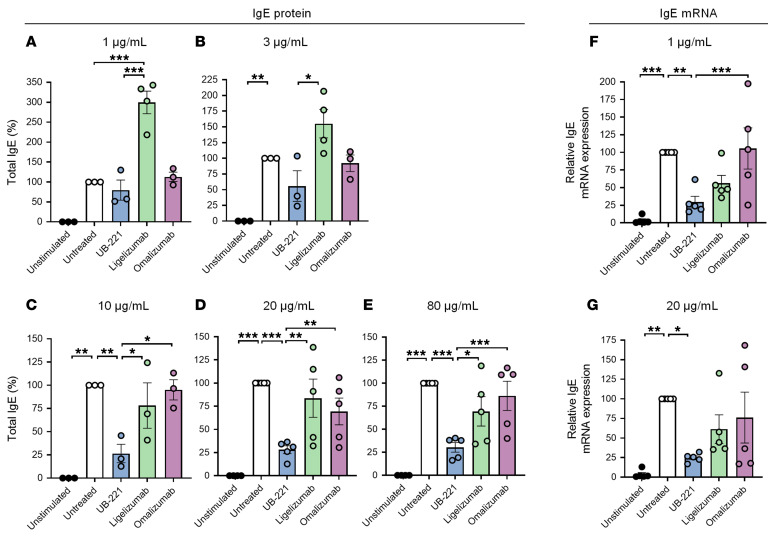
Figure 4. UB-221 induces a pronounced inhibition of IgE protein production and IgE mRNA expression in human PBMCs.
In the presence of UB-221, omalizumab, or ligelizumab (UBP lot), human PBMCs from 3 to 5 healthy donors were stimulated with human recombinant IL-4 and an anti–human CD40 antibody to undergo de novo IgE synthesis. (A–E) The effects on IgE protein production were focused on day 11 by each anti-IgE mAb at doses of (A) 1 μg/mL (n = 3), (B) 3 μg/mL (n = 5), (C) 10 μg/mL (n = 5), (D) 20 μg/mL (n = 5), and (E) 80 μg/mL (n = 5). The total IgE in cell culture supernatant samples was quantified by ELISA. (F and G) In a separate set of donors (n = 5), the effects on IgE mRNA expression in lysates of PBMCs stimulated with human recombinant IL-4 and anti–human CD40 antibody in the presence of UB-221, ligelizumab, or omalizumab were studied at (F) 1 μg/mL or (G) 20 μg/mL. The mRNA expression in cell cultures on day 11 was analyzed by real-time PCR. The percentages of IgE protein/mRNA reduction were calculated based on the total IgE/mRNA levels from the respective untreated cells, which were set as 100%. The percentage reduction values of IgE protein and IgE mRNA are shown in Supplemental Table 1B and Supplemental Table 2, respectively. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Different treatments were compared relative to the untreated group using 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test referenced to untreated controls. *P < 0.05; **P <0.01; ***P < 0.001.