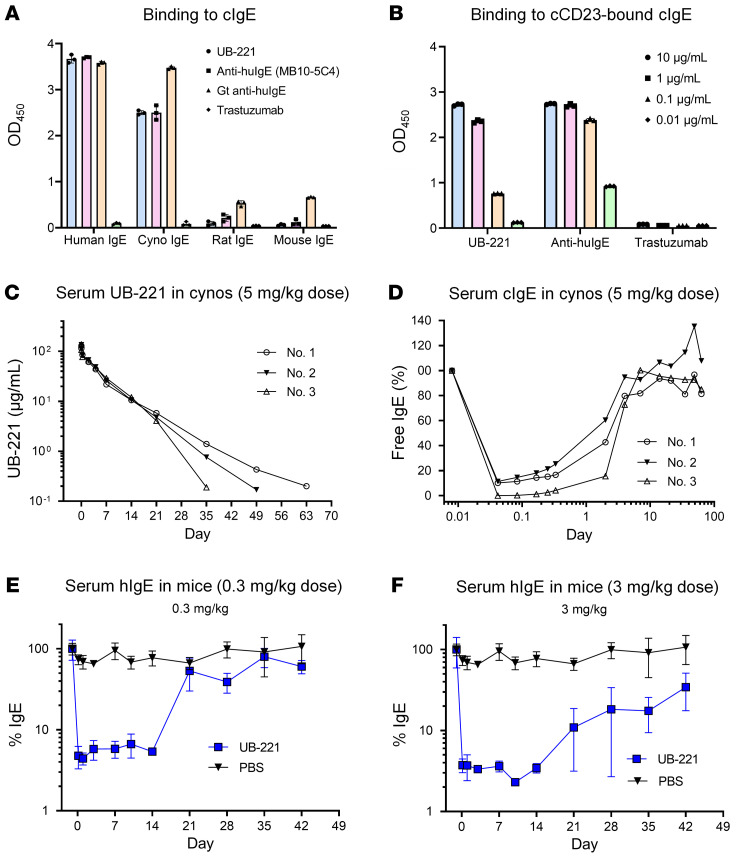
Figure 8. A rapid and pronounced serum free-IgE reduction in cynomolgus macaques and hIGHE-knockin mice after a single i.v. infusion dose of UB-221.
UB-221 can (A) bind to cynomolgus macaque IgE (cIgE), but not rat or mouse IgE, and can also (B) bind to the cCD23-bound cIgE. (C) In cynomolgus macaques (cynos, n = 3) receiving a single i.v. dose at 5.0 mg/kg, UB-221 decayed over time, with a mean half-life of approximately 6.3 days, in which (D) UB-221 was able to induce a rapid reduction in serum free cIgE by 90%–100% in the treated macaques. The basal cIgE levels were at the range of 399 to 434 ng/mL for the 3 macaques. In hIGHE-knockin mice (n = 6 per dose group), a single i.p. dose of UB-221 (E) at 0.3 mg/kg or (F) at 3.0 mg/kg can induce a rapid, greater than 95% reduction in serum free chimeric IgE (mean ± SEM). The basal chimeric IgE levels in the hIGHE-knockin mice were at the range of 416 to 1,365 ng/mL for the 0.3 mg/kg dose group, and of 734 to 3,362 ng/mL for the 3.0 mg/kg dose group.