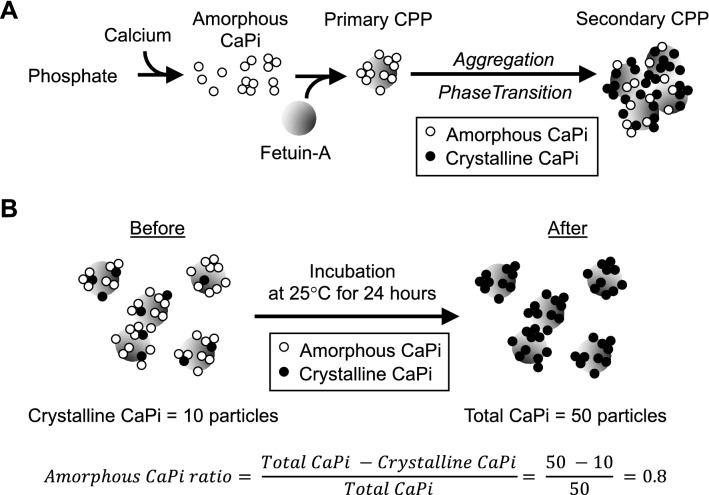
Figure 1.
Calciprotein particles (CPPs) with different properties. (A) A schematic representation of CPP formation and maturation. Precipitates of amorphous CaPi (open circles) are adsorbed by fetuin-A protein (grey circles) to form primary CPPs. Primary CPPs undergo aggregation and transition of CaPi from the amorphous phase to the crystalline phase to become secondary CPPs. (B) A schematic representation of estimation of the amorphous CaPi ratio. Incubation at 25 °C for 24 h induces amorphous-to-crystalline phase transition of CaPi. Because the gel filtration assay can measure crystalline CaPi but not amorphous CaPi, the amorphous CaPi amount (40; the number of open circles) can be estimated as the difference in the number of closed circles between before (10) and after (50) the incubation.