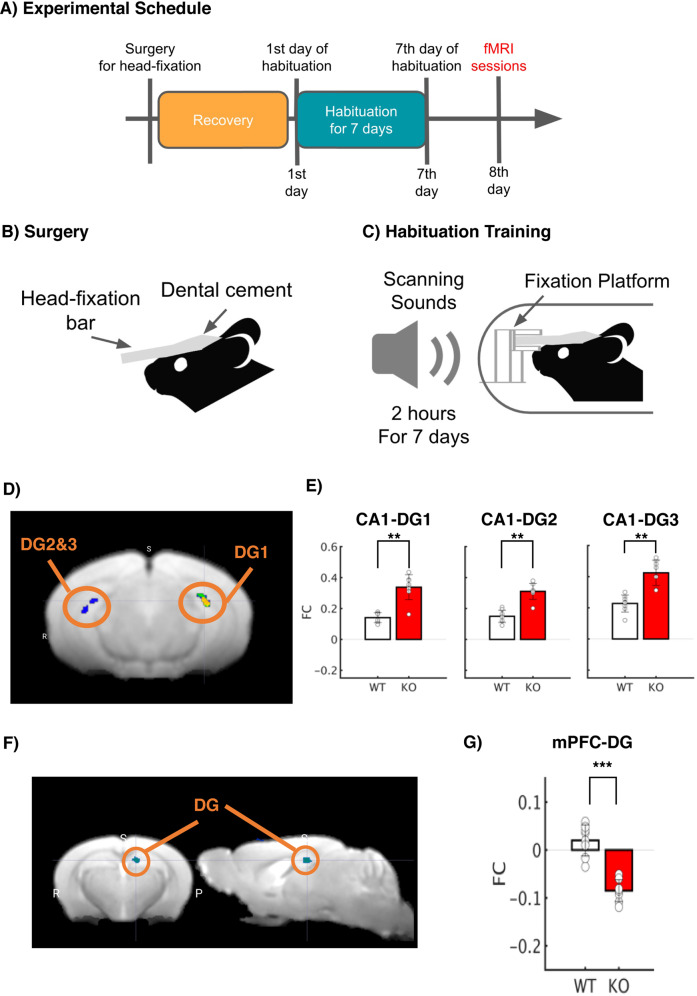
Fig. 2. Deletion of Tob alters brain functional connectivity.
A Experimental Schedule. After surgery to introduce a head-fixation bar on the skull, mice were allowed to recovery. After recovery periods, mice underwent habituation training 2 h for 7 days prior to fMRI sessions. B Surgery. A plastic head-fixation bar was mounted on the skull with dental cement. C Habituation Training. In order to reduce scanning stress, mice were fixated with a fixation platform, and their bodies were constrained in a plastic tube. They were exposed to scanning sounds for 2 h for 7 days in order to reduce stress responses. D Statistical functional map with the seed region, CA1. Average BOLD signals were extracted from bilateral CA1. Seed-based functional connectivity was performed, and a statistical map was visualized (p < 0.05 after cluster correction; Fig. S1). E Functional connectivity with the bilateral CA1 seed. Seed-based FC analysis revealed statistically significant FC in CA1-DG1-3 in the Tob KO group with Mann–Whitney U test (**p < 0.01 with Bonferroni Correction). F Statistical functional map with the seed region, mPFC. Average BOLD signals were extracted from the mPFC. Seed-based functional connectivity was performed, and a statistical map was visualized (p < 0.05 after cluster correction; Fig. S1). G Functional connectivity with the mPFC seed. Seed-based FC analysis revealed statistically significant FC in mPFC-DG in the Tob KO group (***p < 0.001 with Bonferroni Correction).