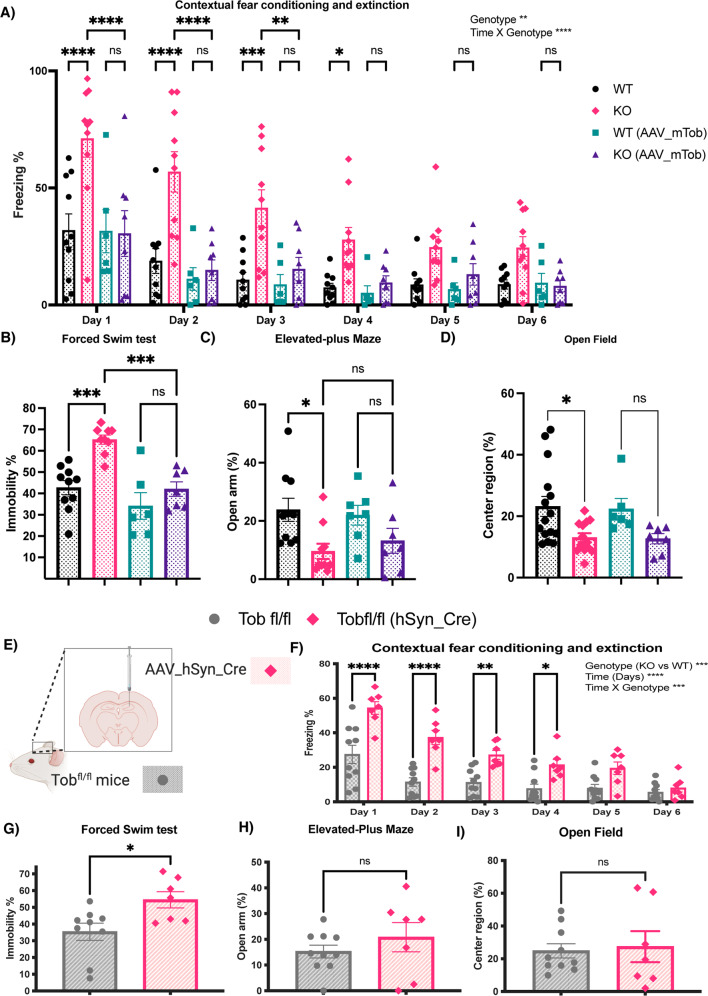
Fig. 4. Tob-KO mice show hippocampal-mediated abnormal stress-related behavior.
Behavioral analyses in Tob-WT and KO mice and after overexpression of mouse TOB using AAV (hSyn-mTob) A–D. A Contextual fear conditioning and extinction expressed as percentage of time spent freezing. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. B The forced swim test presented as a percentage of immobile time. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C Elevated-plus maze showing the percentage of time spent in open arm. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. D Open field test showing the percentage of time spent in center region. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. Behavioral analyses in hippocampal-specific Tob-KO mice (E-I). E Schematic diagram showing the method for generation of hippocampal-specific Tob-KO (hsTobKO) mice through injection of adeno-associated virus expressing Cre recombinase under the hSyn promoter (AAV_hSyn_Cre) in mice having LoxP sequences flanking both sides of the Tob gene (Tobfl/fl). F Contextual fear conditioning and extinction in hsTobKO presented as percentage of time showing freezing. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. G The forced swim test is presented as percentage of time spent immobile. H The elevated-plus maze showed as the time spent in the open arm. I Open field test showing the percentage of time spent in the center region. Unpaired t-test. All values represent means ± SEMs. ns non-significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.