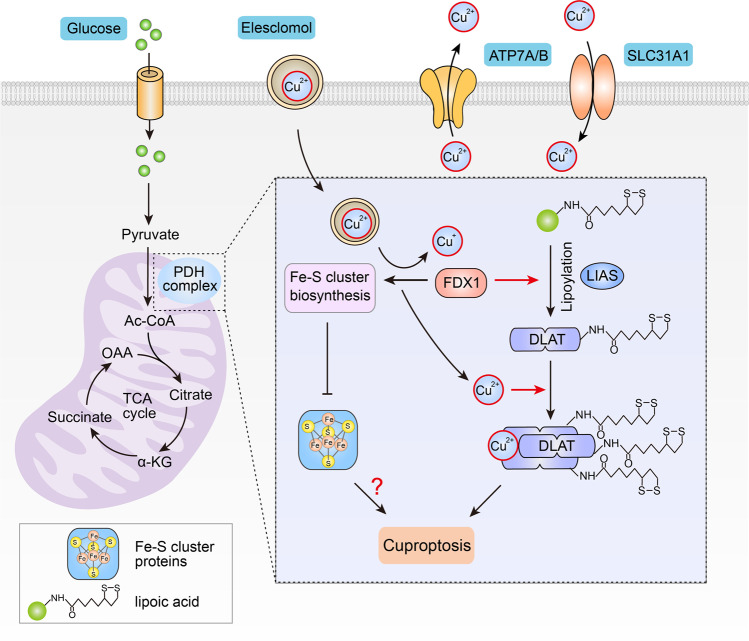
Fig. 1. Schematic model of copper-induced cell death.
In cells that rely on mitochondrial respiration, copper binds to lipoylated DLAT after excessive accumulation due to ionophores or transporters, inducing aberrant oligomerization of DLAT and the formation of DLAT foci. Increased levels of insoluble DLAT causes cellularproteotoxic stress, which further induces cell death. FDX1 is involved in regulating the lipoylation of proteins. In addition, FDX1 reduces Cu(II) to Cu(I), resulting in the inhibition of Fe-S cluster synthesis, which in turn impairs the production of Fe-S cluster proteins.