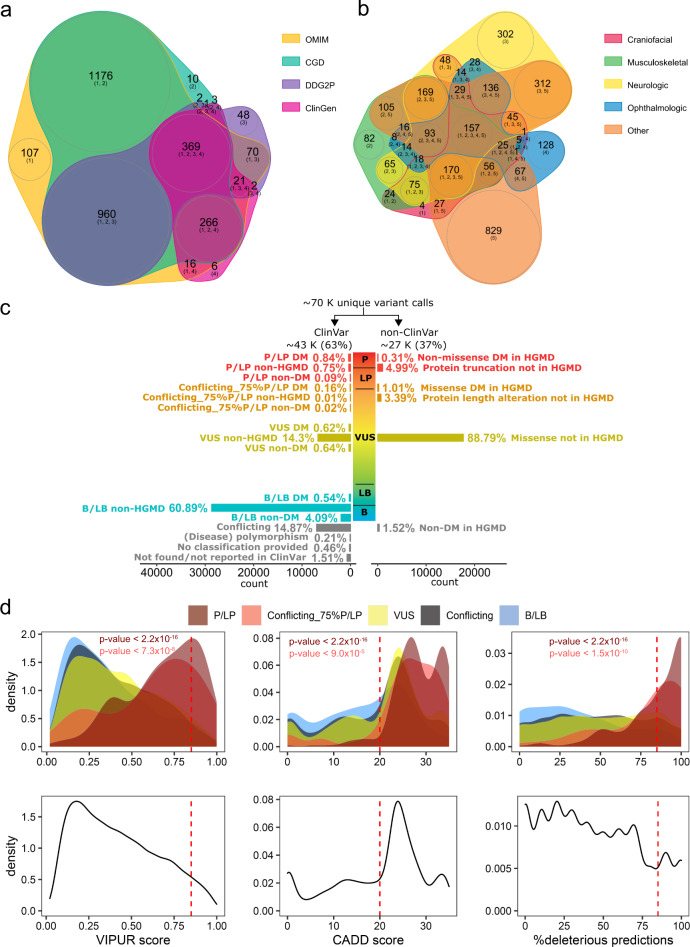
Fig. 1. Genes and variant distributions.
a Venn plot shows numbers of 3,058 AR/XL genes common or distinct in four databases, including the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), the Clinical Genomic Database (CGD), the Development Disorder Genotype - Phenotype Database (DDG2P), and the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen). b Venn plot shows numbers of 3058 AR/XL genes in different manifestation categories according to the CGD manifestation category definition. c Bar plot shows distributions of the percentages of the filtered variants with (ClinVar) and without ClinVar annotation (non-ClinVar) according to their approximate levels of pathogenicity scale. P/LP: pathogenic/likely pathogenic; VUS: variant of uncertain significance; B/LB: benign/likely benign. d Density plots depict distributions of the filtered ClinVar pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP, dark red), ClinVar conflicting with 75%P/LP entries (Conflicting_75%P/LP, red), ClinVar variants of uncertain significance (VUS, yellow), and ClinVar benign/likely benign (B/LB, light blue) missense variants according to VIPUR score (left), CADD score (middle), and the percentage of deleterious predictions of eight conventional in silico prediction tools, including SIFT, PolyPhen2, LRT, MutationTaster, MutationAccessor, FATHMM, PROVEAN, and M.CAP (right). P-values by Welch t-test show the significant difference of the distribution between P/LP and VUS/Conflicting/B/LB (dark red letters) and between Conflicting_75%P/LP and VUS/Conflicting/B/LB (red letters). Red dashed lines indicate cut-offs (VIPUR ≥ 0.85, CADD score ≥ 20, %deleterious predictions ≥ 85%) for “high stringency” missense variants (upper panel). Likewise, density plots depict distributions of the filtered non-ClinVar missense variants (lower panel).