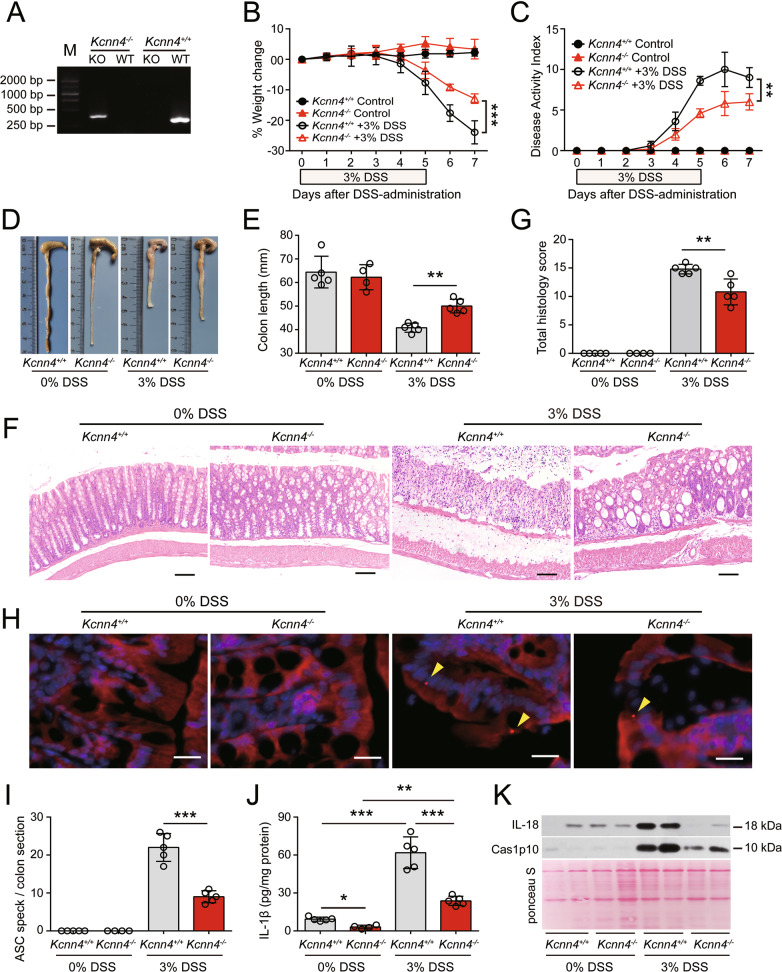
Fig. 9.
KCa3.1 depletion alleviates DSS-induced injury and decreases inflammasome assembly in the colon. Kcnn4−/− and Kcnn4+/+ littermates (9 weeks of age) were treated with drinking water containing 3% DSS for 5 days followed by DSS-free drinking water ad libitum for another two days. A Representative electrophoretic analysis of PCR products from Kcnn4+/+ (320 bp) and Kcnn4−/− (417 bp) mice. B–E KCa3.1 depletion protected mice from DSS-induced weight loss (B), increases in the DAI (C), and shortening of the colon (D, E). F, G KCa3.1 deficiency attenuated colon injury and inflammatory cell infiltration in the DSS-exposed colon. Representative images of colonic sections (H&E.) are shown (F). Scale bars, 100 µm. The histology score of each colonic section was quantified (G). H, I KCa3.1 depletion suppressed ASC speck formation in the DSS-exposed colon. Representative images of colonic ASC immunofluorescence are shown (H). Arrowheads indicate ASC specks. Scale bars, 20 µm. The number of ASC specks in each colon section was quantified (I). J, K KCa3.1 depletion decreased the release of IL-1β (J), Caspase-1p10 (Cas1p10) and IL-18 (K) from DSS-treated colons. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001