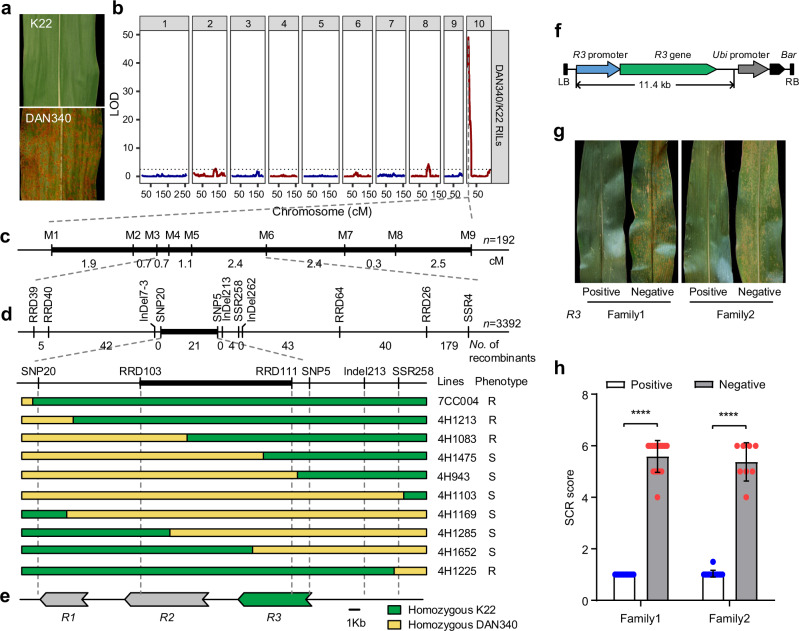
Fig. 1. Map-based cloning of the RppK gene, conferring resistance against southern corn rust.
a Southern corn rust (SCR) disease phenotypes of maize inbred lines K22 and DAN340. b SCR-related QTL locations in the genetic population of DAN340/K22 RILs. LOD, logarithm of odds. c The linkage mapping of the RppK locus based on 192 families delimited it to the region between markers M3 and M6. The numbers below the black rectangle indicate the relative genetic distance (cM) between markers. d High-resolution linkage analysis performed by genotyping 3392 plants of a heterogeneous inbred family (HIF) delimited RppK to a 15.2 kb interval flanked by markers RRD103 and RRD111. The number of recombinants is shown below the markers. Green segments represent the K22 allele, and yellow segments represent the DAN340 allele. The names of lines and the corresponding phenotypes are provided next to the haplotype. R, resistant; S, susceptible. e The RppK region contains three predicted NLR genes, which encode CC-NB-LRR proteins. Scale bar, 1 kb. f Structure of the R3 genomic sequence construct used for generating transgenic maize plants. LB, left border; RB, right border; Bar: Bialaphos Resistance gene. The construct contains the entire R3 genomic DNA sequence, including its 3.1 kb promoter region and a 2.4 kb downstream region. The back arrow indicates the Bar gene. g, h The disease phenotypes and scores of two independent transgenic plant families carrying the R3 genomic sequence. Values are means ± SDs; n = 15, 17, 14, and 8 individual plants of positive and negative lines of family 1 and family 2, respectively. ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test, two-tailed; P = 1.2596E-15, 5.4354E-07). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.