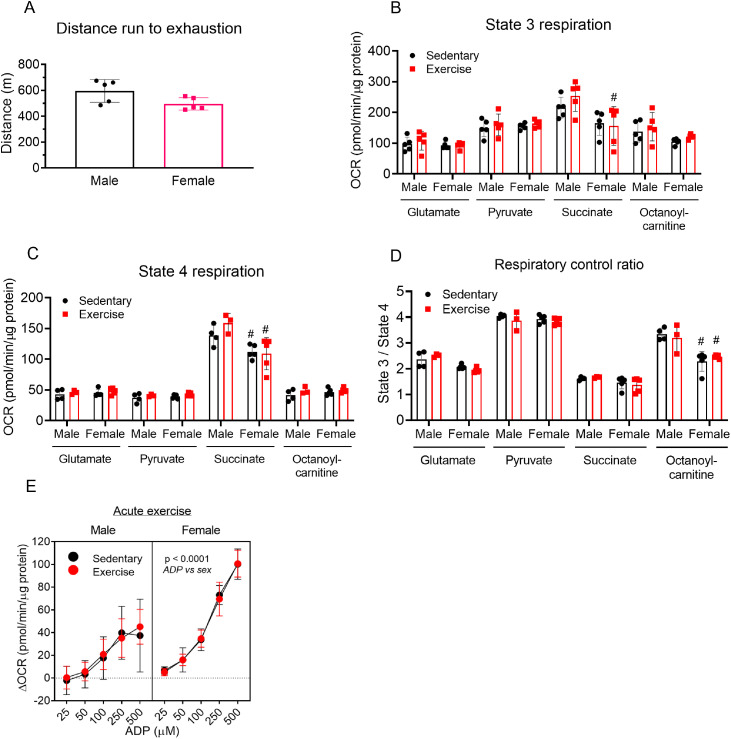
Fig. 7.
Acute exercise has minimal effects on cardiac mitochondrial respiration. Male and female mice were subject to 1 bout of intense exercise followed immediately by isolation of cardiac mitochondria and respiration analyses using glutamate (5 mM), pyruvate (5 mM), succinate (5 mM), or octanoylcarnitine (100 µM) as substrate. (A) Distance run to exhaustion in the high-intensity exercise capacity test; (B) ADP was added to 1 mM to induce state 3 cardiac mitochondrial respiration under each substrate condition; (C) Oligomycin-induced state 4 respiration under each substrate condition; (D) Respiratory control ratio; and (E) ADP sensitivity of cardiac mitochondria provided with pyruvate (5 mM) as substrate and different concentrations of ADP (25–500 µM). n = 5 female mice and 3–5 male mice per group. #p < 0.05 female vs. male, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test performed on B–D and a three-way ANOVA was used to test significance in E. ANOVA = analysis of variance; OCR = oxygen consumption rate.