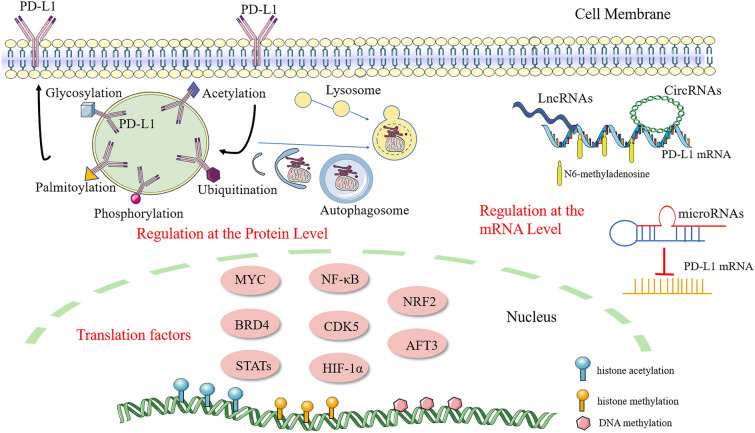
Fig. 2.
Overview of the regulatory mechanisms involved in PD-L1 expression. By attaching to the PD-L1 promoter, numerous transcription factors contribute to the increase of PD-L1 expression. N6-methyladenosine increases PD-L1 expression while DNA methylation, histone modification, and autophagy suppress it. MicroRNAs, including miR-138, miR-138-5p, miR-152, and others shown in Table 1, suppress PD-L1 by directly binding to the 3’UTR of PD-L1 mRNA. LncRNAs and circRNAs are also relevant to PD-L1 expression and tumor immune escape. PD-L1 is upregulated by glycosylation and palmitoylation, which stabilize PD-L1 protein, while ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and acetylation exert the opposite effect