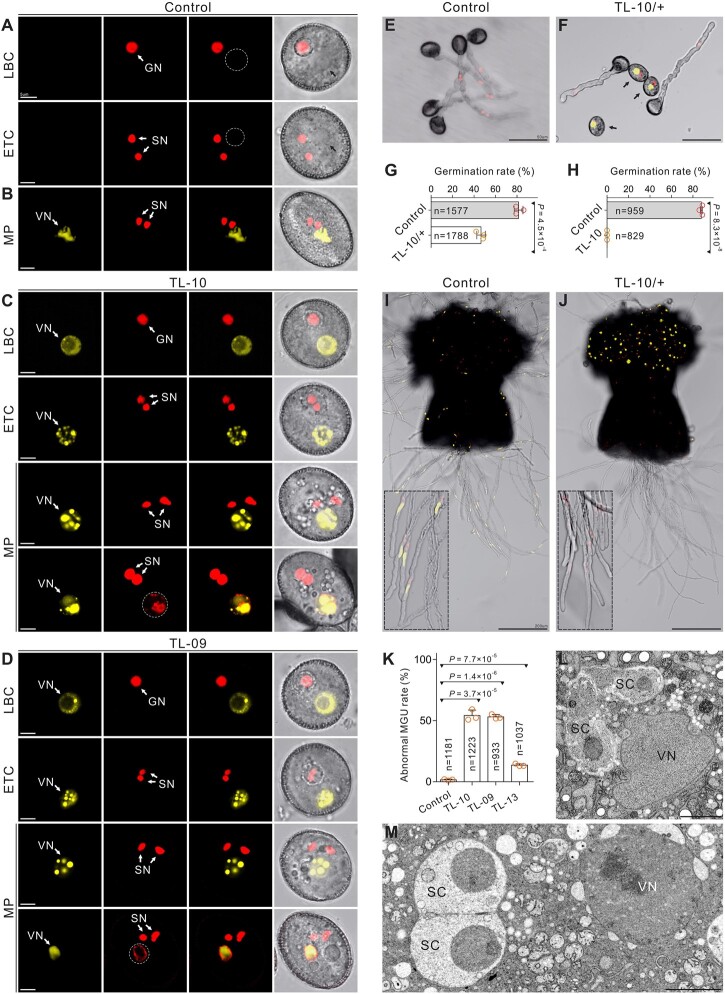
Figure 2.
H3K27me3 is essential for VC identity and functional specification. A and B, Normal morphology in control VCs from the ProHTR10:HTR10-RFP line (A) and ProACTIN11:H2B-GFP ProHTR10:HTR10-RFP double-labeled line (B). Dashed lines and black arrows indicate VN. C and D, The morphology of the strong TL VCs at different development stages. SC formation and VC viability were unaffected, but the abnormal vesicle organization and ectopic HTR10-RFP signal were detected in the mature pollen from TL-10 (C) and TL-09 (D) lines. Dotted lines indicate the ectopic HTR10-RFP signal in VN. E and F, In vitro pollen germination assay of the ProHTR10:HTR10-RFP line (E) and TL-10/+ carrying the HTR10-RFP marker (F). Arrows indicate the pollen unable to germinate. G and H, Comparison of the in vitro pollen germination rate between control and TL-10/+. Results are from three independent experiments. I and J, In vivo–in vitro pollen germination assay following pollination of WT pistils with control pollen (ProACTIN11:H2B-GFP ProHTR10:HTR10-RFP double-labeled line [I]) and TL-10/+ pollen (J), respectively. Dotted box in (I) displays the MGU in pollen tubes. Dotted box in (J) indicates that TL-10 pollen failed to form tubes and all the observed tubes are from normal pollen. K, Statistical analysis of the abnormal MGU construction in control and TL lines. Results are from three independent experiments. Statistical significance is determined by Student’s t test (***P < 0.001) and the error bars show sd. TEM of WT (L) with normal MGU and TL-10 (M) pollen with abnormal MGU construction. Scale bars, 5 μm (A–D), 50 μm (E, F), 200 μm (I, J), and 2 μm (L, M). LBC, late bicellular; ETC, early tricellular; MP, mature pollen.