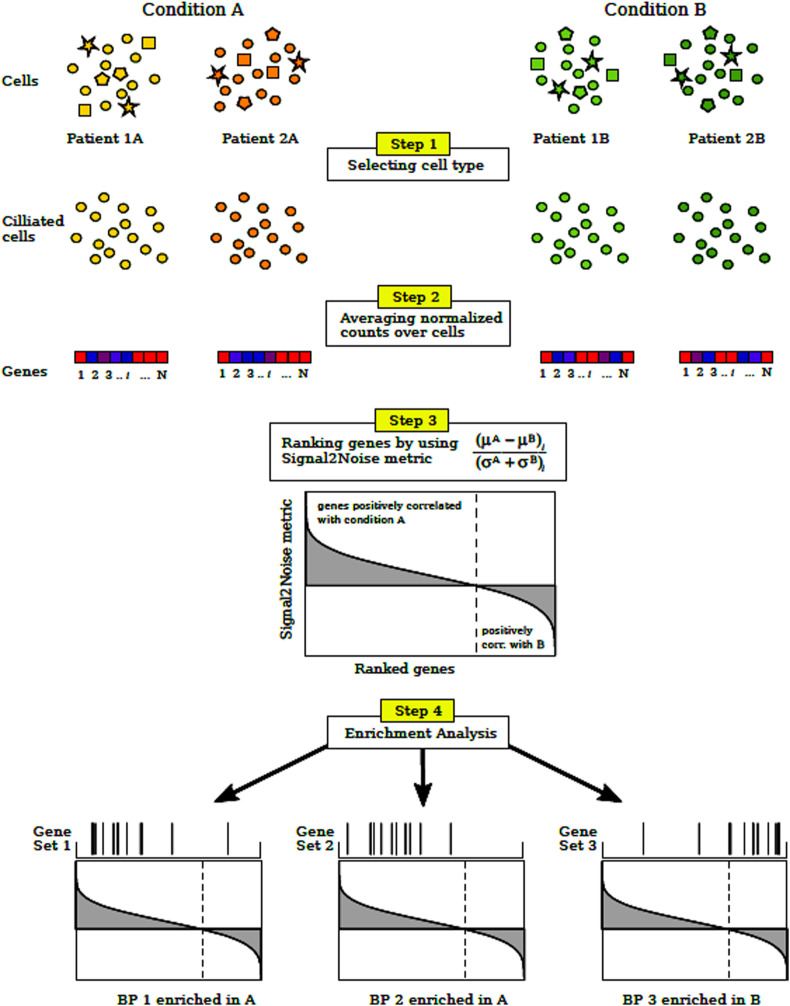
Fig. 1.
Methodology flow chart
Step 1: The specific type of cells is selected from each patient (ciliated cells in our case).
Step 2: Normalized counts for each gene are averaged (arithmetic mean) over the selected cells population of each patient, obtaining the average expression profile of ciliated cells for each patient.
Step 3: Signal2Noise metric is computed among the patients of the two conditions of interest. μA(μB) and σA(σB) are the mean and standard deviation of gene expression levels computed in the previous step for patients under condition A (B). Then, the genes are ranked by decreasing order of the metric value.
Step 4: Finally, it is determined if the ranked gene set, associated with a given biological process (BP), shows statistically significant, concordant differences between the two conditions. This last step can be performed with different BPs or even with gene set associated with molecular functions or miRNAs.