Figure 5.
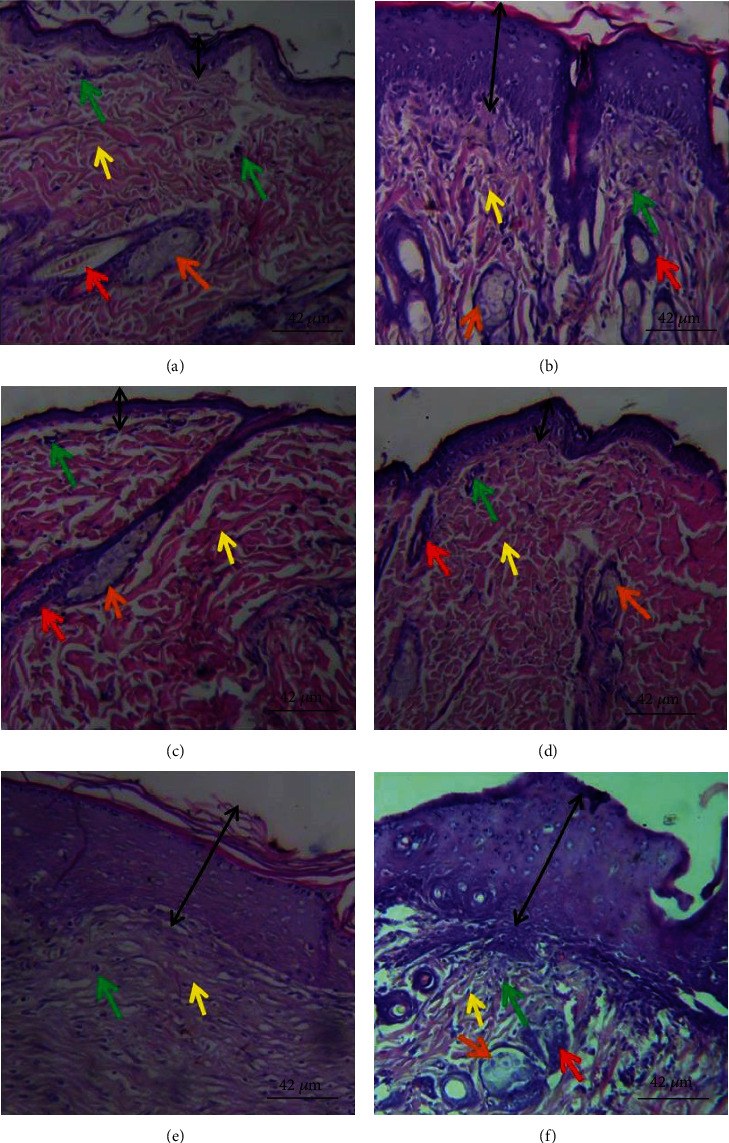
Histological section of healed wound tissue showing epidermis (black double headed arrow) and dermis. (a) Thin epidermis and slightly fibrotic granulation dermis with mild eosinophilia of collagen fibers, moderate inflammatory cell infiltration, and few sebaceous glands. (b) Thick epidermis and slightly fibrotic granulation dermis with mild eosinophilia of collagen fibers, severe inflammatory cell infiltration, coagulation in the hair follicle, and moderate abundance of sebaceous glands. (c) Thin epidermis and loose granulation dermis with widespread eosinophilic collagen fibers and moderate inflammatory cell infiltration, widespread coagulation in the hair follicle, very few hair follicle, and sebaceous glands. (d) Thin epidermis and slightly fibrotic granulation dermis with focal eosinophilia of collagen fibers, very few inflammatory cell infiltrations, and coagulation in the hair follicle. (e) Thick epidermis with appreciable keratin layer. Dermis is fibrotic with few inflammatory cell infiltration, absence of hair follicle, and sebaceous gland. (f) Thick epidermis and loose granulation dermis with moderate inflammatory cell infiltration and few sebaceous glands. Magnification: ×400. (a) Model, (b) vehicle, (c) 1% SSD, (d) 0.3% PCFHE, (e) 1% PCFHE, and (f) 3% PCFHE. PCFHE: P. clappertoniana fruit husk extract; SSD: silver sulfadiazine.
