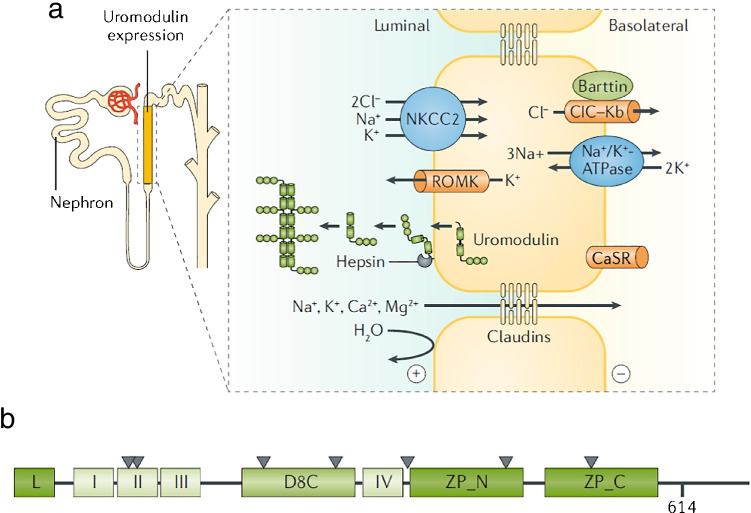
Fig. 3.
Site of production and structure of uromodulin. Uromodulin is mainly produced by the cells that line the thick ascending limb (TAL), a segment involved in the reabsorption of NaCl and divalent cations, while being not permeable to water. Uromodulin is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein which traffics to the apical membrane of the cells, where it is cleaved by the serine protease hepsin and released in the urine where it forms large polymers. These polymers form the matrix of the urinary casts. The predicted structure of uromodulin contains a leader peptide (L); four EGF-like domains (I to IV); a cysteine-rich D8C domain; a bipartite C‑terminal Zona Pellucida domain (ZP_N and ZP_C) connected by a linker; and a GPI-anchoring site at position 614. The seven N‑glycosylation sites are indicated by triangles. Figure adapted from Devuyst et al. [11, 12]