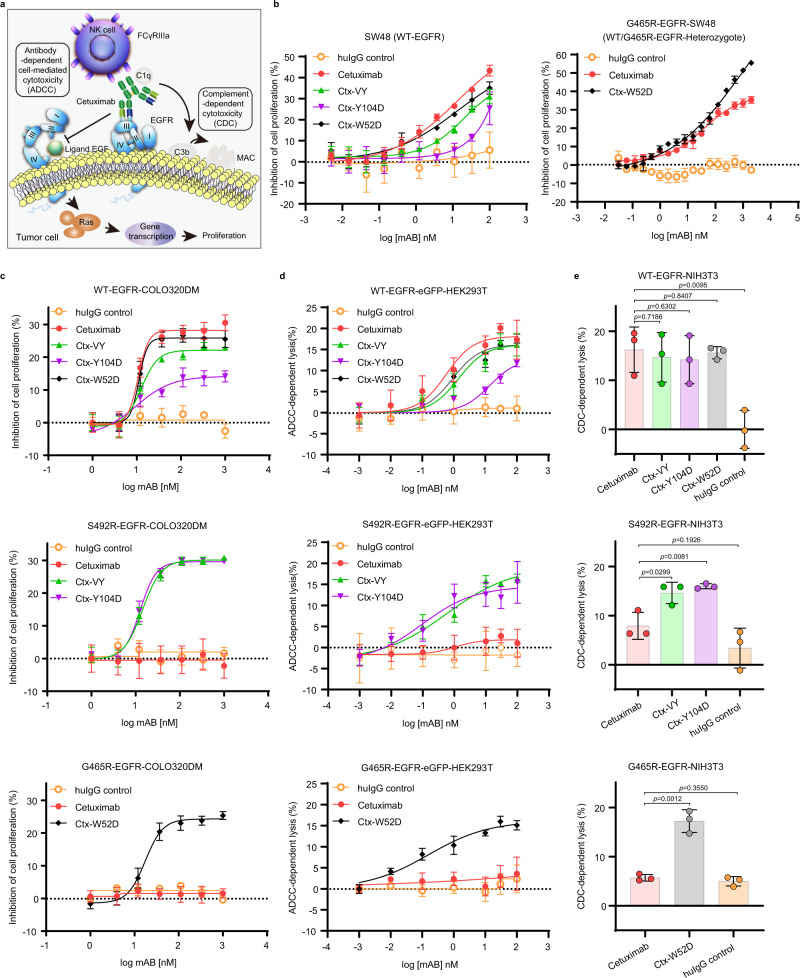
Fig. 6. The cetuximab variants inhibited the growth of wild-type EGFR- and S492R/G465R-mutated EGFR-positive cells in vitro.
a The mechanisms of action underlying the antitumor activities of cetuximab. b The in vitro efficacy of cetuximab and the cetuximab variants in inhibiting the proliferation of cetuximab-sensitive/resistant cells. The wild-type EGFR cell line SW48 (WT-EGFR) and SW48 cells stably expressing full-length EGFRG465R (G465R-EGFR-SW48) were used as model cell lines, and treated with serial concentrations of antibodies for 3 days. Cell viability was determined by a CCK-8 assay. c The in vitro efficacy of cetuximab and the cetuximab variants in inhibiting the proliferation of cells in the established CRC xenograft model. WT-EGFR-COLO320DM cells, S492R-EGFR-COLO320DM cells and G465R-EGFR-COLO320DM cells were used as model cell lines, and treated with serial concentrations of antibodies for 3 days. Cell viability was determined by a CCK-8 assay. d The ADCC activity of cetuximab and the cetuximab variants. LDH release was detected after hours of coincubation of PBMC effector cells and WT-EGFR-eGFP-HEK293T or mutant-EGFR-eGFP-HEK293T target cells at an E:T ratio of 40:1. e The CDC activity of cetuximab and the cetuximab variants. WT-EGFR-NIH3T3 cells and mutant-EGFR-NIH3T3 cells were incubated with serial concentrations of antibodies in the presence of 10% human serum for 2 h, and cell viability was measured by a CCK-8 assay. All above experiments were performed in triplicates. The bars indicate the mean ± SD values (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, N.S. means not significant; two-tailed Student’s t-test). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.