FIGURE 3.
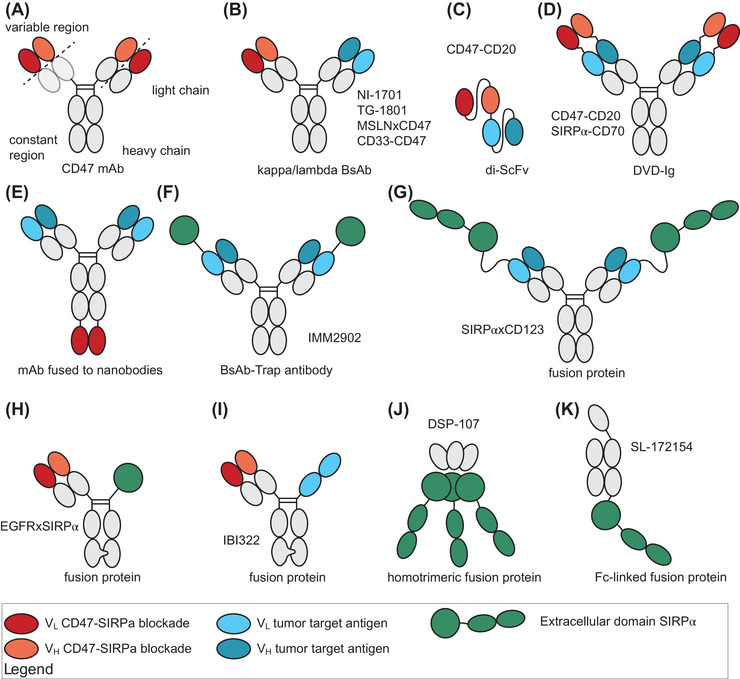
Different bifunctional CD47‐targeting antibodies (bispecific antibodies, bsAbs) and fusion proteins compromising signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). (A) A normal monoclonal antibody (mAb) demonstrating the different regions used in bifunctional proteins. (B) Kappa/lambda bsAb compromised of a kappa and lambda light chain and are fused by a common heavy chain with an active IgG1 domain. (C) Di‐single‐chain variable fragment (di‐ScFv) is compromised of the variable regions of RTX and CD47 mAb fused with a linker. (D) The dual‐variable‐fragment domain is compromised of a full antibody fused to the variable region of a CD47‐ or SIRPα‐directed antibody. (E) A full RTX antibody is fused to a CD47‐directed nanobody (a single‐domain antibody fragment derived from a naturally occurring heavy‐chain IgG antibody). (F) A bispecific trap antibody that is comprised of a human epithelial growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)‐directed full antibody and the variable domain of the extracellular domain (ED) of SIRPα. (G) A fusion protein comprising the full CD123 antibody fused to the ED of SIRPα. (H) A fusion protein compromised of the VH VL of an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody fused to the ED of SIRPα using the knobs‐into‐holes technique. (I) A fusion protein compromised of VH VL of a CD47 mAb fused with a programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD‐L1) mAb that consists of an Fc domain with two VL. (J) A homotrimeric fusion protein compromised of the ED of 4‐1BBL and three EDs of SIRPα. (K) An Fc‐linked fusion protein compromised of the ED of SIRPα that is linked through an inactive IgG4 Fc domain with the ligand of CD40. DVD‐Ig, dual‐variable domain immunoglobulin; MSLN, mesothelin; VH, variable domain of the heavy chain; VL, variable domain of the light chain
