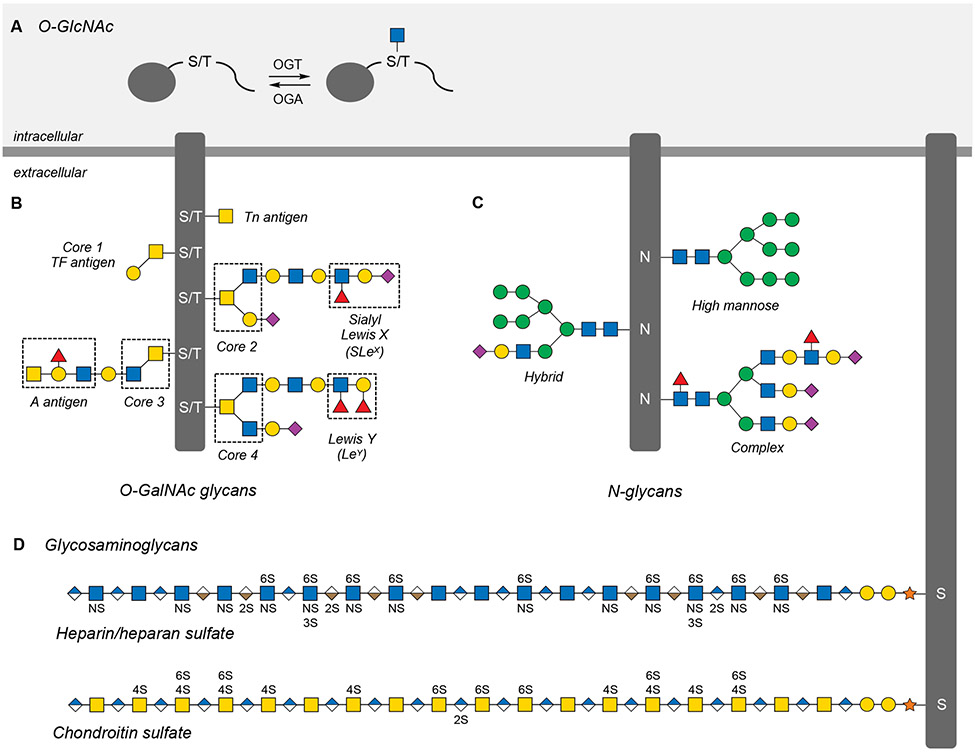
Figure 2. Major glycan classes in mammals.
(A) O-GlcNAcylation is the dynamic and reversible addition of N-acetylglucosamine to Ser and Thr residues on thousands of intracellular proteins.
(B) O-GalNAc or mucin-like glycans are a broad class of O-linked extracellular glycans categorized by one of eight core structures that can be elaborated with a number of glycan antigens.
(C) N-glycans are branched glycans attached to Asn residues of extracellular proteins and are categorized by the number and composition of their antennae branching from a conserved core structure.
(D) Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear extracellular polysaccharides that can be sulfated at different hydroxyl and amine positions along the length of the glycan chain.