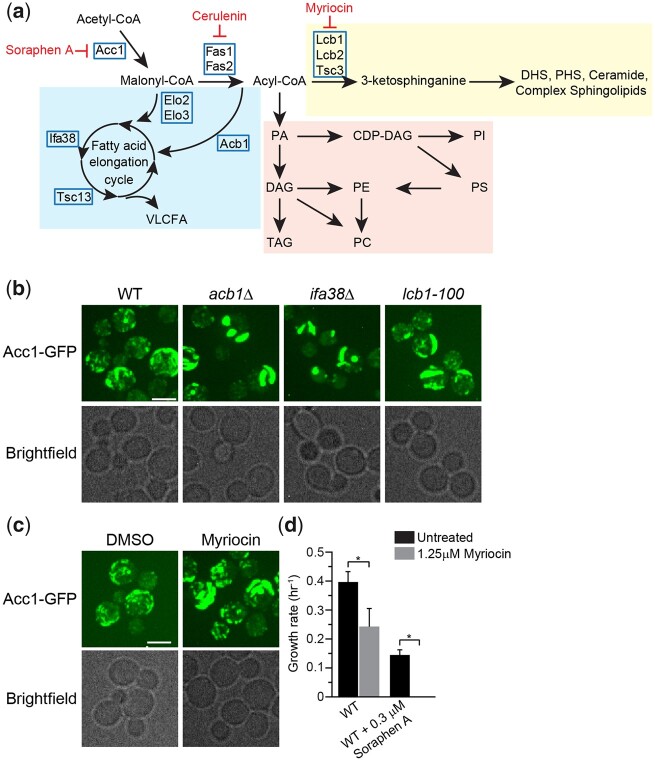
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of the FA elongation cycle and sphingolipid metabolism induces the formation of thick rod-like structures of Acc1-GFP. a) Schematic of the FA elongation and sphingolipid metabolism pathway that includes genes that encode the enzymes within pathway and pharmacological inhibitors Myriocin and Cerulenin. b) acb1Δ, ifa38Δ, and lcb1-100 mutants impact the localization of Acc1-GFP. Wild-type (YKB 3954), acb1Δ (YKB 4601), ifa38Δ (YKB 4629), and lcb1-100 (YKB 4609) cells expressing endogenously tagged Acc1-GFP were grown to early-log phase at 30°C in YPD and immediately assessed for Acc1-GFP localization within the cells. Representative brightfield and fluorescent images are shown. Scale bar: 4 µm. c) Myriocin, a SPT inhibitor, induces the formation of thick rod-like structures of Acc1-GFP. Wild-type (YKB 3954) cells expressing endogenously tagged Acc1-GFP were grown to early-log phase at 30°C in YPD. Cells were then again diluted to an OD600 of 0.1 in YPD with or without 1.25 µM Myriocin, and then grown for 3 h at 30°C before imaging Acc1-GFP localization within the cells. Representative brightfield and fluorescent images are shown. Scale bar: 4 µm. d) Myriocin significantly increases the toxicity of Sor A. Wild-type (YKB 1079) cells were grown to early-log phase diluted to an OD600 of 0.1 in YPD with or without 0.3 µM Sor A and/or 1.25 µM Myriocin, automated growth curve analysis was performed at 30°C for 48 h and growth rate calculated from 3 biological replicates. Error bars denote the standard error of the mean (SEM). n = 3, *P < 0.05 determined using a 2-way ANOVA test with a Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.