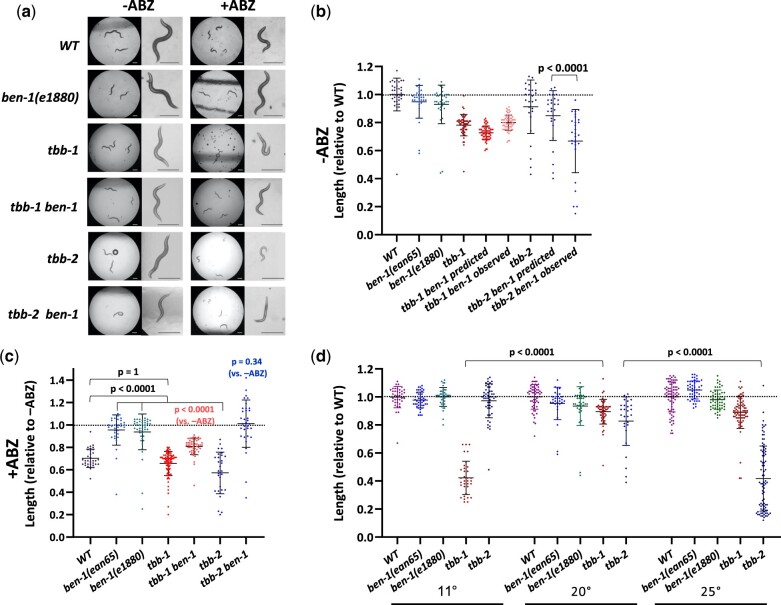
Fig. 1.
Genetic interactions of β-tubulin genes. Unless otherwise stated, experiments represent 3 days of growth at 20°C, during which time controls grew to L4/Adulthood. a) Images of the effects of ABZ on strains at low and high magnification. tbb-2 mutants may be hypersensitive to ABZ and tbb-2 ben-1 double mutants grown in the absence of ABZ resemble the wild type exposed to drug. Scale bars = 250 µm. The spots in some images are crystals that sometimes form on NGM. b) Worm lengths, in the absence of drug were normalized to the average length of the wild type. A representative wild-type sample is shown, but values of each strain were normalized to the wild type grown in parallel. The distribution of expected lengths of the double mutants of tbb-1 and tbb-2 with ben-1(e1880) was determined by multiplying each single mutant value by the average of ben-1(e1880). The observed value tbb-2 ben-1 double mutant was lower than expected. c) Effects of ABZ on tubulin mutants normalized to the average length of the same strains grown in parallel off drug. The tbb-2 mutant appears more sensitive but was completely rescued (average near 1.0) by a mutation in ben-1. The tbb-1 mutant showed normal sensitivity (but see Fig. 2) and only showed partial rescue of the ben-1 defect. d) Although both tbb-1 and tbb-2 single mutants grew well at 20°C, the tbb-1 mutant was cold sensitive and the tbb-2 mutant was heat sensitive. Growth was measured after 8 days at 11°C, 3 days at 20°C, and 2 days at 25°C, during which times controls grew to L4/Adult. Note that the tbb-1 and tbb-2 20°C data are that same as that used in (b). Mean and standard deviations are indicated. Two-tailed Mann–Whitney Rank-Sum test were used to calculate P-values. Supplementary Fig. 5 contains raw data in microns.