Fig. 2.
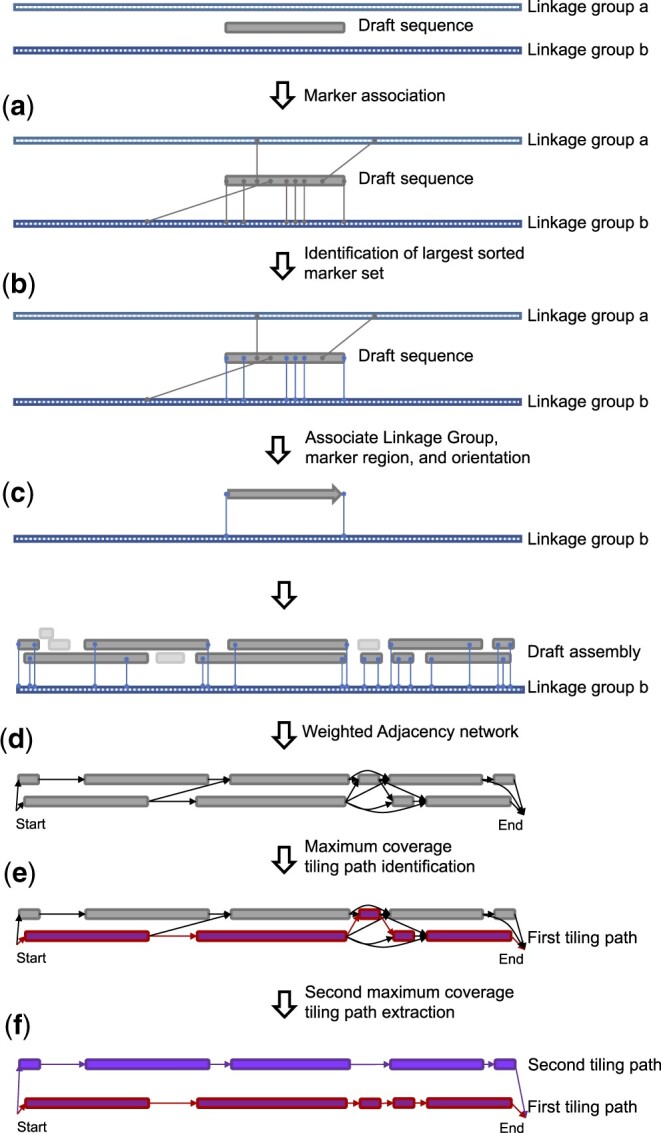
The HaploSplit procedure using genetic markers as input. a) The procedure identifies marker positions in the draft sequences. b) The longest sorted set of markers is identified for each draft sequence. c) Each sequence is assigned to a unique genomic region in the map (linkage group) and oriented. d) A directed adjacency network of nonoverlapping sequences is built for each linkage group connecting all sequences with no overlapping ranges of genetic markers. Sequences sharing markers are placed in separate network paths. e) The tiling path that maximizes the number of covered markers is selected for the first haplotype. f) Sequences belonging to the first haplotype are removed from the adjacency network and the second-best tiling path is used to scaffold the second haplotype.
