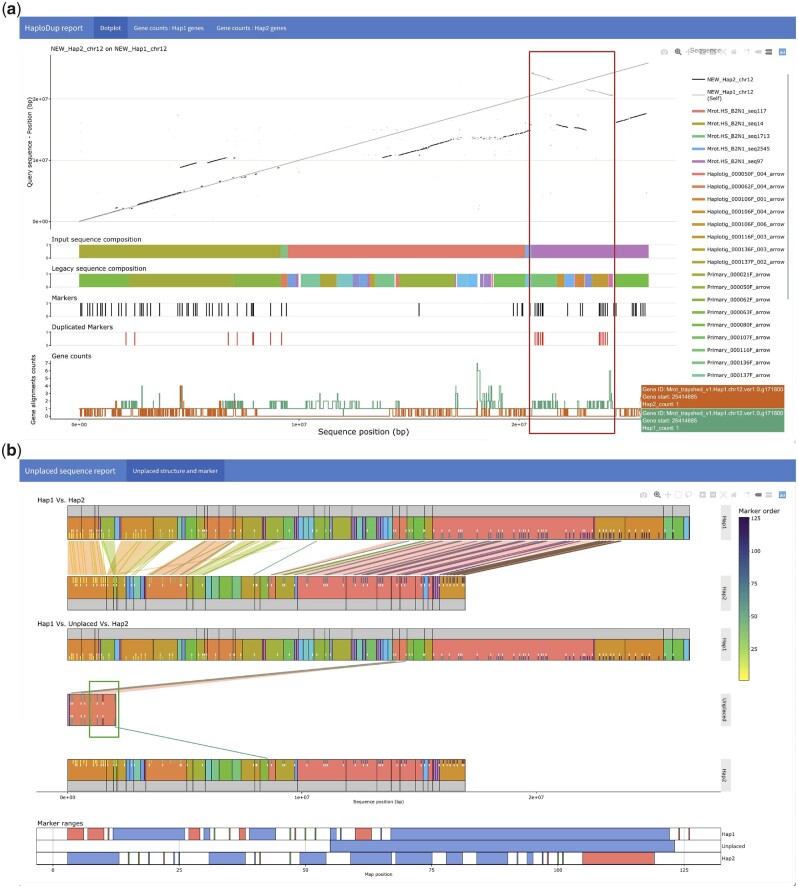
Fig. 3.
Example of HaploDup’s interactive reports. The figure reports 2 static screenshots exemplifying HaploDup interactive output. a) Assembly quality control of M. rotundifolia chromosome 12 Haplotype 1: whole-sequence alignment of both alternative haplotypes on Haplotype 1, legacy contig and hybrid scaffold composition of Haplotype 1, position of the genetic markers and the duplicated markers in Haplotype 1, number of significant alignment(s) per gene of Haplotype 1 in each alternative haplotype. In this example, the composition in legacy contigs and position of duplicated markers indicate that both alleles (primary contig and haplotig) and both marker copies were placed in a hybrid scaffold (overlayed box). b) Unplaced sequence quality control: Marker content is compared between pseudomolecules and unplaced sequences to evaluate conditions that prevent the inclusion of a specific unplaced sequence. Color-coding is used for better contextualization. Markers are color-coded based on their order in the map. The structure of pseudomolecules and unplaced sequences are represented with color-coded blocks. Blocks identify the composition in terms of draft assembly sequences, color coding is used to show the existing relationships between the composing sequences (e.g. primary to haplotig relationships). In this example, the presence of a marker (overlayed box, the dark marker on the right of the contig) in the unplaced sequences far from its expected position on the map extends the expected coverage of the map to the end of the linkage group and prevents placement in any haplotype scaffold.