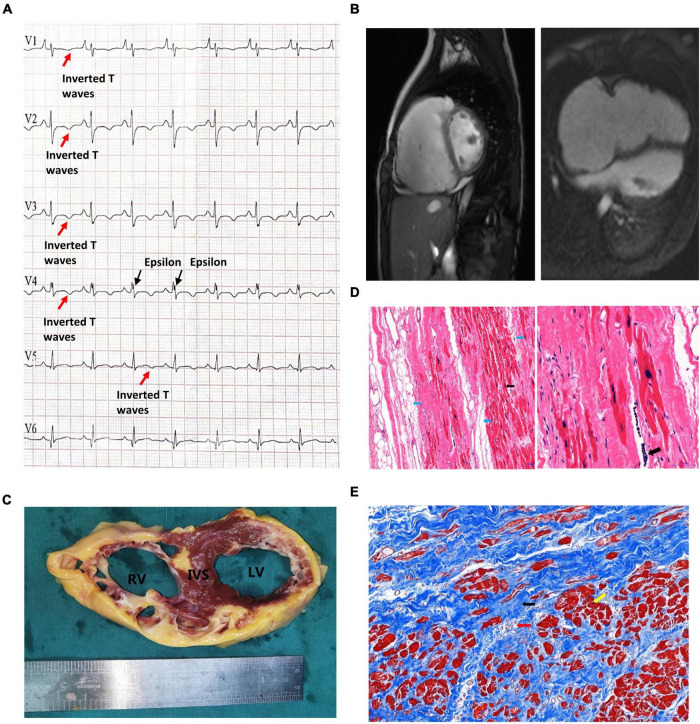
FIGURE 1.
Clinical presentation of the proband. (A) The patient’s preoperative ECG showed inverted T waves in lead V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5, with typical Epsilon waves visible in V4. (B) Preoperative cardiac MRI of the patient indicated that the right atrium was significantly enlarged, the right ventricular wall was thinner, the right ventricular wall edge was localized in many places, and the amplitude of myocardial contraction of the right ventricle was significantly reduced. (C) The myocardium was replaced by extensive fibrous adipose tissue in the wall of the right ventricle (RV), the right ventricle was bag like and thinly dilated, part of the ventricular septum (IVS) was adipose, and part of the myocardium in the anterior and lateral wall of the left ventricle (LV) was replaced by adipose fibers. (D) HE staining of the myocardium of the right ventricle: Left: the blue arrow indicates the adipose tissue, and the myocardium of the right ventricle is surrounded by the adipose tissue and divided into cords. The black arrow shows abnormal hypertrophic cardiomyocytes with large, dark-stained nuclei and oddly shaped nuclei, broken muscle fibers in the cytoplasm of the cardiomyocytes (magnified 100×). Right: The black arrow indicates the presence of inflammatory cell infiltration between cardiomyocytes at magnified 200×. (E) Masson staining of the myocardium of the right ventricle. Note that the myocardium (the yellow arrow) is surrounded by large amount of fibrous adipocytes (the black arrow) and divided into cords or islands. The collagenous fiber bundles around small blood vessels (red arrows) are increased.