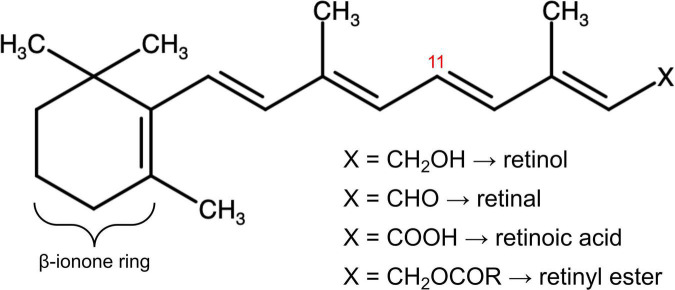
FIGURE 1.
The molecular structure of vitamin A in its multiple forms. The chemical group denoted X defines retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and retinyl esters depending on its composition. Stereoisomeric 11-cis and 11-trans retinoids depend on the three-dimensional arrangement of the vitamin A molecule around the double bond at the eleventh carbon residue, labelled in red. The ß-ionone ring, modified in synthetic forms of vitamin A, is also labelled.