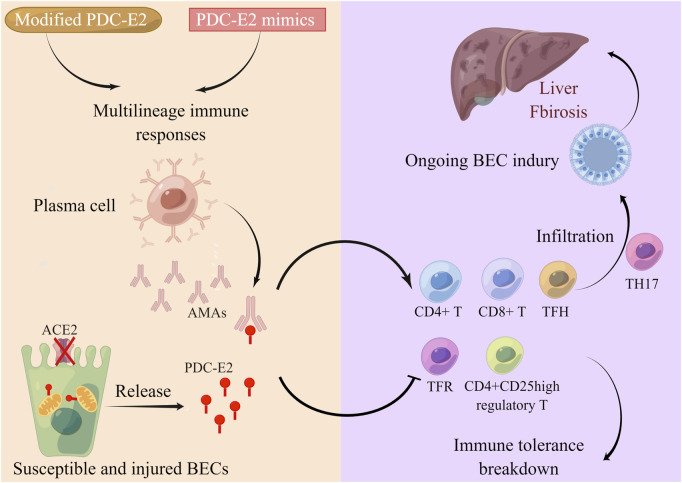
FIGURE 1.
Systemic autoimmune response in PBC pathogenesis. The main AMA targeting PBC-E2 is expressed on the inner mitochondrial membrane. When exposed to environmental PDC-E2 mimic or modified PDC-E2, multilineage immune responses are triggered to attack the BECs. Plasma cells then generate disease-specific AMAs to target immunodominant PDC-E2 epitopes on the BECs, causing BEC injury. AE2 is localized on the apical domain of BECs. BECs with dysfunctional AE2 are susceptible to apoptosis, which further exposes PDC-E2 to circulating AMAs, resulting in extensive cellular injury. Autoreactivity-suppressing CD4+CD25high Tregs and T follicular regulatory (TFR) cells are downregulated in PBC, accounting for the disruption of immune tolerance. Proinflammatory effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and TFH cells infiltrate the portal tracts, while Th17 infiltration is also observed in PBC targeting damaged cholangiocytes, which leads to the advanced fibrosis stage of PBC.