TABLE 2.
Localization frequencies of and complementation by GFP-FtsQ and GFP-FtsQ swap protein constructs
| Construct | Structurea | Total no. of cells scored | % Localization frequency (mean ± SD)b | Complementation of the following mutation:
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tsc | Nulld | ||||
| GFP-FtsQ | 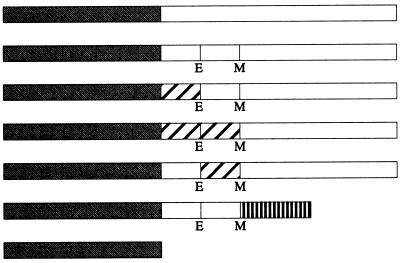 |
715 | 60 ± 3 | + | + |
| GFP-QQQ | 696 | 44 ± 7 | + | + | |
| GFP-FQQ | 703 | 37 ± 8 | + | + | |
| GFP-FFQ | 654 | 35 ± 10 | + | ± | |
| GFP-QFQ | 599 | 30 ± 6 | + | ± | |
| GFP-QQL | 150 | 0 | − | ND | |
| GFP alone | 60 | 0 | − | − | |
Open boxes represent domains of FtsQ. Hatched boxes represent domains derived from MalF. Stippled boxes denote GFP. The box with vertical bars represents the periplasmic domain of FtsL. E and M indicate the borders of the transmembrane domain where the restriction sites for EagI and MscI, respectively, were introduced. These sites caused the following amino acid changes in FtsQ: T23G, W48L, M49G, and E50D. Diagrams of fusion proteins are not to scale. The cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains of FtsQ contained 24 and 25 amino acids, respectively, while those of MalF contained 16 and 25 amino acids. The periplasmic domain of FtsQ contained 227 amino acids, while that of FtsL contained 64 amino acids.
Determined from three independent sets of experiments. Strains EC442, JOE192, JOE193, JOE194, JOE196, and JOE257 were grown in parallel cultures, fixed, and scored for localization as described in Materials and Methods.
Complementation of the ftsQ1(Ts) allele was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The strains used were JOE225, JOE226, JOE228, JOE229, JOE230, JOE231, and JOE259. +, complementation; −, no complementation.
Complementation of the ftsQ::TnphoA50 null allele was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The strains used were JOE204, JOE206, JOE210, JOE212, JOE214, and JOE216. +, complementation; ±, partial complementation; −, no complementation; ND, not determined.
