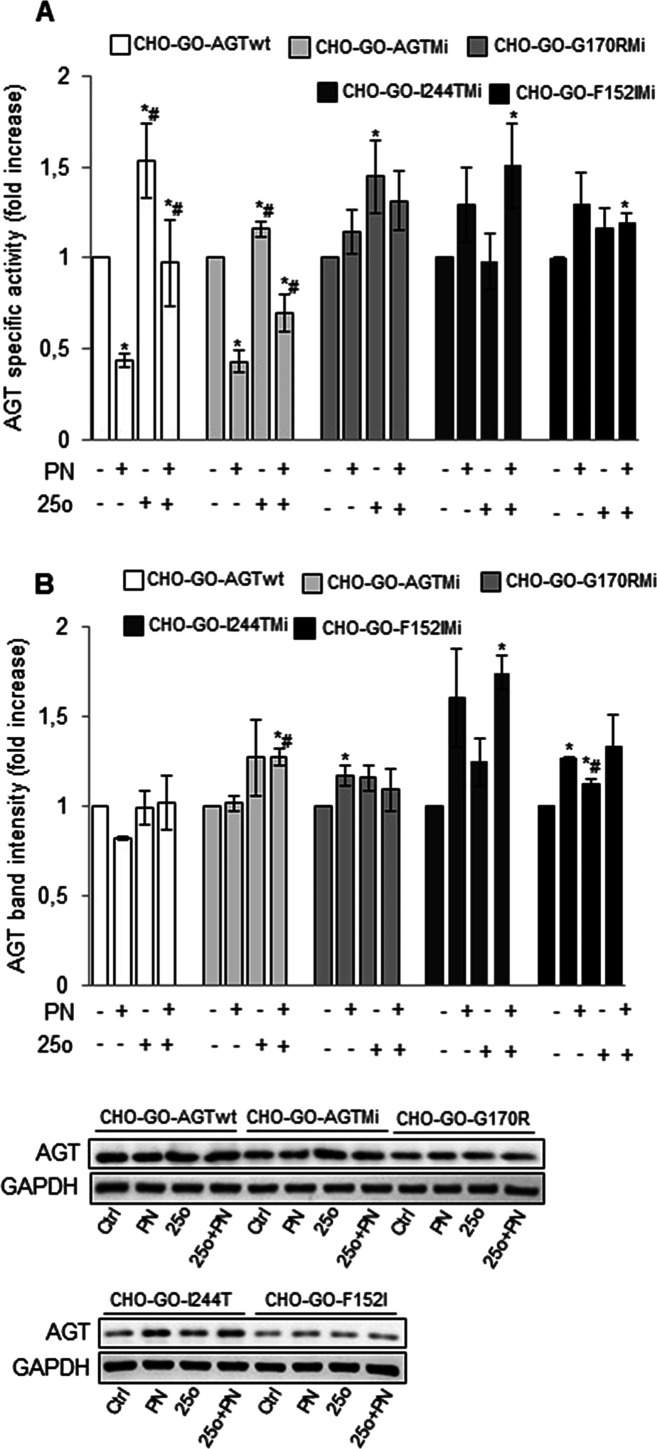
Figure 7.
Action of compound 25o as pharmacological chaperone for common pathogenic AGT variants. CHO-GO-AGTwt, CHO-GO-AGT-Mi, CHO-GO-G170R-Mi, CHO-GO-I244T-Mi, and CHO-GO-F152I-Mi cells were grown for 7 days in the absence or presence of 50 μM 25o and 10 μM PN. At the end of treatment, cells were detached and lysed, and the soluble fraction of each sample used for (A) AGT enzymatic activity determination. The AGT specific activity of control cells of each clone was assumed to be 1 to help assess the changes (CHO-GO-AGTwt cells: 191 ± 10 nmol of pyruvate/min/mg protein; CHO-GO-AGT-Mi: 132 ± 9 nmol of pyruvate/min/mg protein; CHO-GO-G170R-Mi: 54 ± 7 nmol of pyruvate/min/mg protein; CHO-GO-I244T-Mi: 28 ± 5 nmol of pyruvate/min/mg protein; CHO-GO-F152I-Mi 24 ± 5 nmol of pyruvate/min/mg protein). Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs respective control cells. #p < 0.05 vs respective PN-treated cells. (B) AGT expression level quantification. AGT levels in control cells of each clone were assumed to be 1 to help assess the changes. GAPDH has been used as loading control. The images are representative of one out of three separate experiments. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs respective control cells. #p < 0.05 vs respective PN-treated cells.