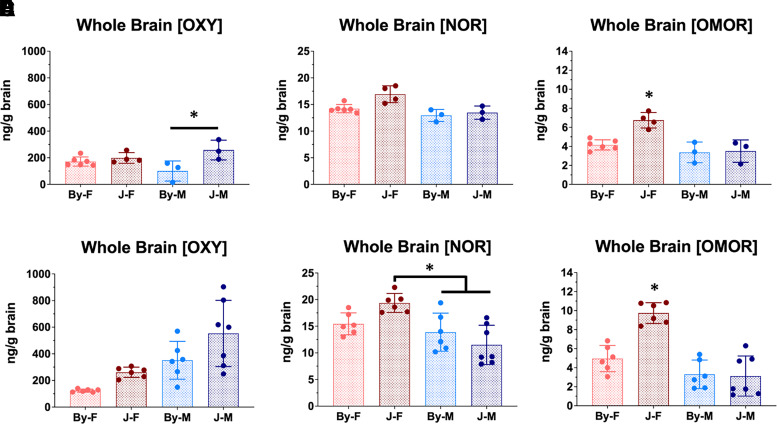
Fig. 2.
BALB/cJ mice show elevated whole brain concentrations of OXY, NOR, and OMOR compared with BALB/cByJ mice at 30 minutes postinjection of OXY (1.25 mg/kg, i.p.). (A–C) All analysis was conducted using a two-way ANOVA considering substrain and sex; error bars represent standard deviation. For the first cohort of mice, we observed an effect of substrain on brain concentrations of all compounds. We also detected significant main effects of sex and interactions of sex with substrain for [NOR] (P = 0.048) and [OMOR] (P = 0.005). In both cases, this effect was driven by increased drug concentrations in J females (Tukey’s post hoc *P = 0.022–9.9e-4). Sample sizes from left to right in panel A were6, 4, 3, and 3. (D) For the second cohort of mice in which there were slightly different procedures (see Materials and Methods), for whole brain [OXY] we observed an effect of substrain (P = 0.007) and sex (P = 3.1e-4) but no interaction. (E) For whole brain [NOR], there was no effect of substrain, but there was a significant effect of sex (P = 5.2e-4) and a sex × substrain interaction (P = 0.014) that was driven by a significant increase in J females vs. J males (Tukey’s post hoc *P = 5.2e-4). (F) Finally, for whole brain [OMOR], there were main effects of substrain (P = 0.004) and sex (P = 1.5e-6) and a substrain × sex interaction (P = 8.7e-4) that was driven by the increase in [OMOR] in J females compared with all three other groups (Tukey’s post hoc *P < 2.1e-4). Sample sizes from left to right (panel A) were 6, 6, 6, and 7.
* = Tukey's Post Hoc T-test p < 0.05.