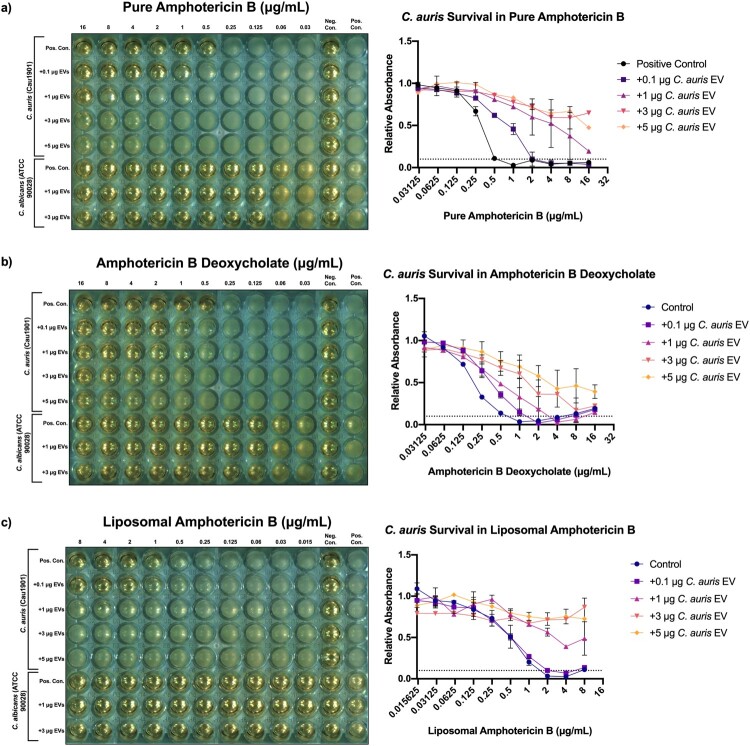
Figure 3.
The addition of Candida auris extracellular vesicles to in vitro C. auris cultures increases their resistance to amphotericin B in a dose-dependent manner, but not C. albicans. Left: Representative European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) antifungal susceptibility testing (AFST) broth microdilution plate incubated with treatment groups, n = 3. Right: mean relative absorbance of AFST plates inoculated with C. auris Cau1901 measured at 450 nm after 24 h, n = 3. (a) Pure amphotericin B. (b) Water soluble amphotericin B deoxycholate. (c) Liposomal amphotericin B.