Figure 1.
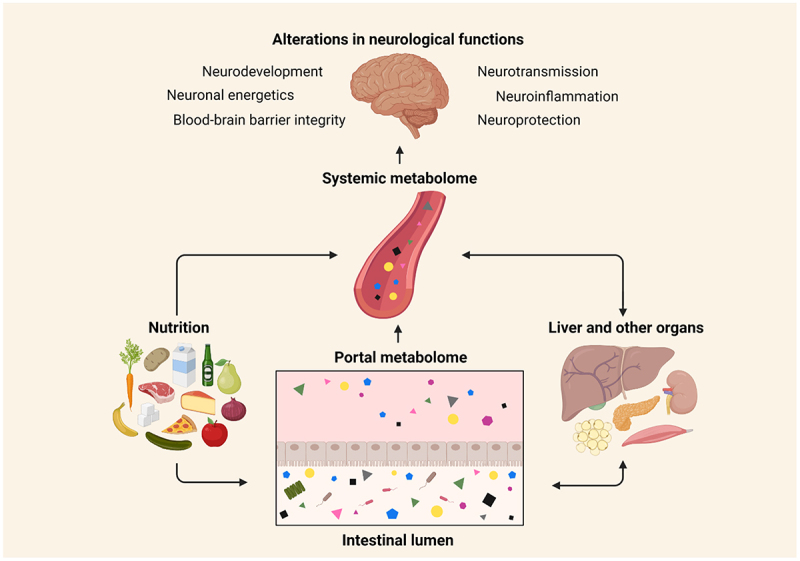
Host metabolic homeostasis and neurological impact.
The portal metabolome reflects the intestinal metabolism of dietary compounds. After processing by the liver, a pool of metabolites will reach the systemic circulation. The systemic metabolome is a dynamic metabolic signature reflecting the interaction between the diet, gut microbiota, liver, and other organs. Metabolites can influence the functioning of all organs, including the brain by modulating a range of metabolic pathways related to neurological functions. (Figure created with Biorender.com)
