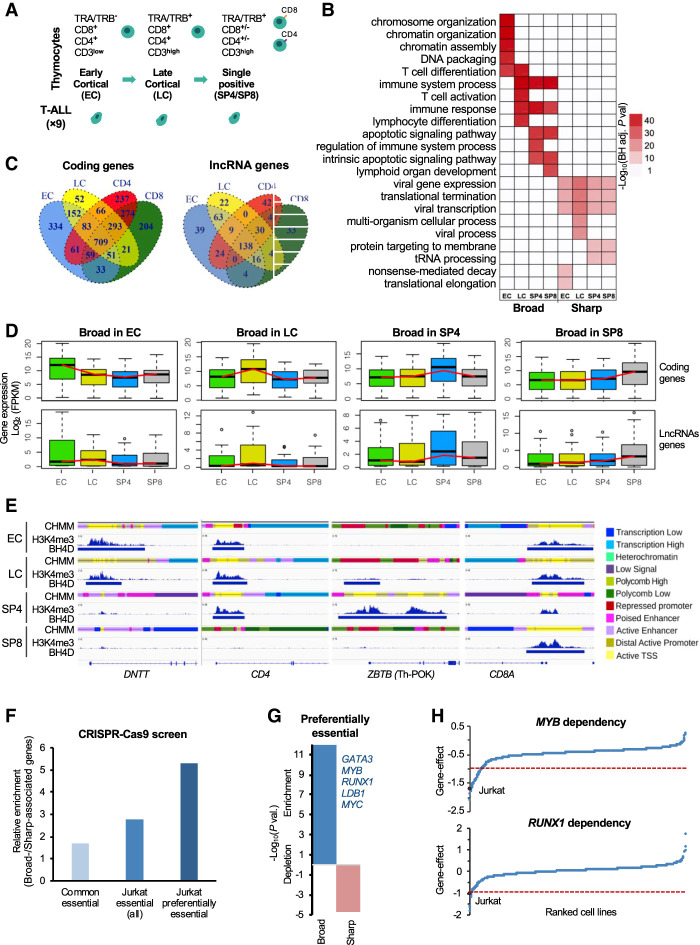
Figure 1.
Dynamics of broad H3K4me3 domains during early T cell differentiation. (A) Schematic representation of the major stages of human thymopoiesis. (B) Top enriched pathways associated with broad H3K4me3 domain genes. (C) Overlap of broad H3K4me3 domains associated with coding or lncRNA genes between the thymic T cell subpopulations. (D) Box plot displaying the distribution of gene expression in each T cell subpopulation of genes associated with broad H3K4me3 domains in the indicated subpopulation. (E) Examples of dynamic broad H3K4me3 domain loci. H3K4me3 ChIP-seq signals, broad domains, and chromatin state (CHMM) profiles are shown for the indicated thymocyte subpopulations. The color-code is indicated at the right of the panel. (F) Ratio between the percentage of broad- and sharp-associated genes that were defined as commonly essential, essential in Jurkat cells, or preferentially essential in Jurkat cells based on the DepMap data set of loss-of-function CRISPR-Cas9-based screen for essential genes (for details, see Methods). (G) Significant overlap between broad- and sharp-associated genes in Jurkat cells and preferential essential genes was assessed by the hypergeometric test. (H) Example of two preferentially essential genes associated with broad H3K4me3 domains in Jurkat cells. The gene effect from the loss-of-function CRISPR-Cas9-based assays in all the cell lines is shown, and the Jurkat cell line is highlighted.